Did you know that the grammatical structure of conditionals varies according to the possibility of the event? We use the simple present tense when something is a scientific fact or general truth. And my previous sentence is an example of a zero conditional.
Read on as I discuss the uses and constructions of the zero conditional in grammar. I also provided several sentence examples and a worksheet to help you master the lesson. Let’s go!
What is the Zero Conditional?
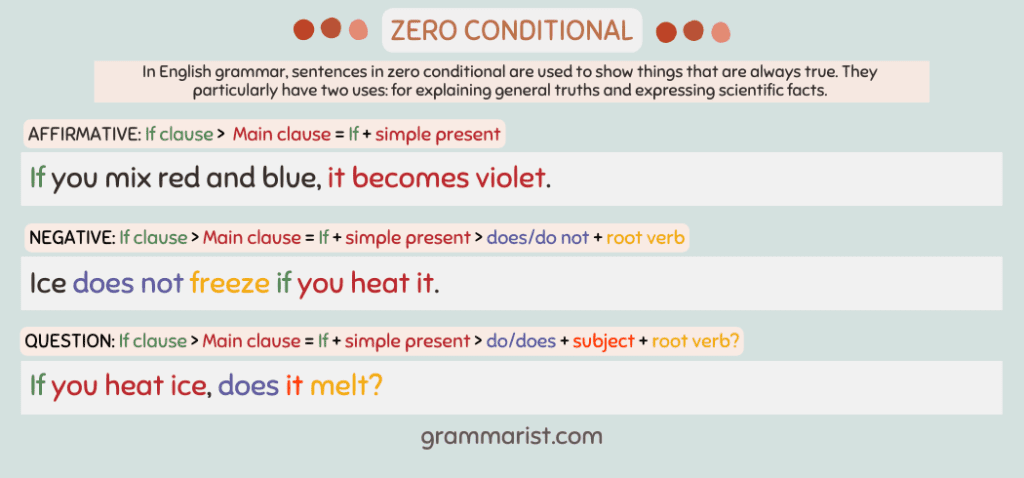
In English grammar, sentences in zero conditional are used to show things that are always true. They particularly have two uses: for explaining general truths and expressing scientific facts. You’ll see them used in non-fiction writing, documentaries, biographies, etc.
To recall, a conditional describes the outcome of things that could take place in the present or future or might have happened in the past. It is composed of the if clause and the result.
Use the zero conditional when the result always happens. For instance, when we heat ice, it always boils. It’s a scientific fact. Below is another example.
- If it rains, the grass gets wet.
In this sentence, the if clause is if it rains, and the outcome is the grass gets wet. This statement is always true because the rain causes grass to be wet. In other words, it shows absolute certainty. Compare it to the statement below, which is in the first conditional.
- If I pass the exam, I’ll celebrate with my family.
This sentence is not a general truth because the speaker is not 100% sure they will pass the exam. It only shows the future consequence of something realistic or possible.
Here is another example of a zero conditional sentence:
- When you subscribe to the website, you receive a monthly email newsletter.
While the statement is not a scientific fact, this statement is always true because it might be a company policy.
You can even use zero conditional to relay instructions. Just use the imperative form for the main clause. For example:
- If Jessa calls, tell her to meet me behind the mall at 5:00 PM.
Here are more zero conditional examples.
- If the teacher teaches the lesson, the students take the quiz.
- If people overeat, they gain weight.
- Snakes bite when they are provoked.
- You get a free membership in this country club if you take tennis lessons.
- Babies cry if they are hungry.
- Ask the teacher if the instructions are unclear to you.
- If you can’t find me, ask for help from the concierge.
- Send the customized lessons by email if you want me to learn about foreign grammar concepts.
- Please arrive at the venue early if you want front-row seats.
You can change the word if into when in zero conditionals without changing the sentence’s meaning.
What is the Formula for Zero Conditional?
The zero conditional form follows this English grammar structure:
- If clause > main clause
= If + simple present > simple present
= If this thing happens > that thing happens.
For example:
- If you mix red and blue, it becomes violet.
This structure is relatively easy to remember because both clauses use a single tense. Remember that the order of the clauses can be rearranged into:
- Main clause > if clause
= simple present > if + simple present
= That thing happens > if this thing happens.
For example:
- Red and blue become violet if you mix them.
You can also replace if with when.
- When you mix red and blue, it becomes violet.
- Red and blue become violet when you mix them.
The reason behind using the simple present tense is that the conditional always results in the same outcome. Therefore, the process occurs regularly and is permanent. Make sense?
For negative sentences, we use the word not.
- If clause > main clause
= If + simple present > does/do not + root verb
= If this thing happens, that thing does not happen.
For example:
- Ice does not freeze if you heat it.
Question sentences follow this structure:
- If clause > main clause
If + simple present > do/does + subject + root verb?
For example:
- If you heat ice, does it melt?
Can We Use Unless in Zero Conditional?

You can also use unless in the if clause to replace if and when. Unless is a subordinating conjunction that means except if. Use it to introduce a situation where the statement is not true. For example:
- Ice does not melt unless it’s heated.
The main clause validates the idea that ice does not melt but makes an exception in the if clause. According to the speaker, ice only melts when it’s heated.
Below are more examples of zero conditional sentences with the conjunction unless.
- You don’t lose weight unless you burn more calories than you eat.
- Blue does not turn into violet unless you mix it with red.
- Pluto is not a planet unless it meets the criteria that the IAU uses to define a full-sized planet.
Reviewing the Zero Conditional
I hope my guide familiarized you with the grammatical construction of the zero conditional. Remember what I said that the zero conditional only has two uses:
- When the situation is real and possible.
- When using an imperative sentence.
Both the if clause and the main clause in a zero conditional sentence follow the simple present tense. You can also use the conjunctions if, when, and unless for the if clause.