There are several kinds of pronouns. But one characteristic of pronouns found among all types is that they represent a person, place, object, animal, or idea.
Keep reading as I explain the difference between pronouns of different kinds. I also provided a list of each type of pronoun and some examples of how to use them in sentences.
What is a Pronoun?
Pronouns are not only composed of he, she, it, and they. This part of speech refers to any word that replaces nouns, noun phrases, also known as antecedents. Other examples of pronouns that might surprise you are somebody, what, each other, and that.
Like nouns, pronouns can be subjects of a verb or objects of a verb or preposition.
There are several types of pronouns aside from personal pronouns like he, she, it, and they. Reflexive pronouns, interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns are other types.
Personal Pronouns
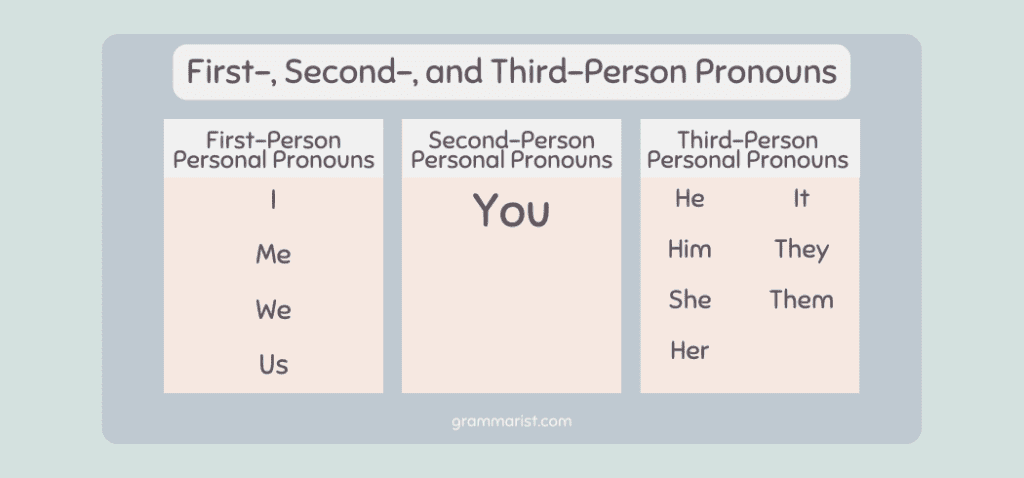
Personal pronouns in grammar are a simple substitute for a proper noun or name of a person or other common nouns.
Some also consider pronouns for animals, objects, and events personal pronouns. They allow us to speak and write concisely to avoid repeating names throughout our writing.
Pronouns, like nouns, can be subjects or objects. Helpful resources in grammar require the use of correct pronouns according to their functions in sentences.
For example, subject pronouns should use he and she instead of him and her. Object pronouns should include us and them instead of we and they.
The correct use of personal pronouns in sentences also depends on the point of view. First-person pronouns include I, we, me, and us. The second-person pronoun is you.
Lastly, a third-person pronoun replaces a third-person noun, including he, she, it, they, him, her, it, and them. Try differentiating between the plural and singular third-person pronouns.
Some recommend using antecedents in the same sentence. But since there are no absolutes in grammar, then it’s acceptable not to include it in the sentence if the reader knows what you’re discussing.
Personal Pronoun Examples
Personal pronouns can be singular pronouns, replacing a singular noun or noun phrase. Here’s a singular personal pronoun list.
- You.
- I/me.
- He/him.
- She/her.
- It.
They can also be plural, replacing plural nouns and noun phrases.
- You.
- We/us.
- They/them.
Personal Pronouns Used in Sentences
Here are some examples of personal pronouns in a sentence.
- James is guilty. He is responsible for the graffiti on the wall.
- You and I should meet tomorrow. We can get coffee and shop for clothes.
- I like Thai food. It’s my favorite.
- Have you seen Julius and Phil? Bella said they were in the other building a while ago.
- Is that us in the photo? We look so young there.
- The members that the adviser chose are them.
How Do You Avoid Using He or She in Writing?
Instead of using he or she in writing, try using they. Many style guides recommend gender-neutral and gender-inclusive pronouns to represent every person. They is a concise catch-all pronoun that can function as a singular pronoun.
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns replace a subcategory of nouns called possessive nouns. A possessive noun is a noun that shows ownership or direct connections. They typically have an apostrophe and s in the end.
Pronouns of possession simplify constructions, showing possession of a noun by replacing it. For example, instead of saying Rose’s cars are expensive, you can say Her cars are expensive.
A possessive pronoun in grammar can also function as a possessive adjective. It clarifies who or what owns something. In the sentence above, her modifies the noun cars.
Possessive Pronouns Examples
Here’s a list of possessive pronouns.
- My, mine.
- Your, yours.
- His.
- Her, hers.
- Its.
- Our, ours.
- Their, theirs.
One common mistake in the practice of possessive pronouns is mistaking its and it’s. Remember that its is the possessive pronoun, while it’s is a contraction of it is.
Possessive Pronouns Used in Sentences
Here are some examples of possessive pronouns in sentences to help you achieve perfect grammar.
- That cell phone of yours is too loud.
- Is this towel hers? I think I saw her holding it yesterday during gym class.
- My group answers this worksheet. It’s ours.
- This room used to be hers before I moved in.
- His love for her is overflowing. (His as a possessive adjective modifying love).
- Our trust for each other is unbreakable. (Our as a possessive adjective modifying trust).
Relative Pronouns

A relative pronoun is a type of pronoun that introduces a dependent clause and connects it to independent clauses. These common pronouns are found at the beginning of a noun clause.
One of the pronoun rules for this type is that they serve as subjects and objects in the sentence. Logically, you should use a subjective case pronoun like who when it functions as a subject. Use an objective case pronoun like whom when it’s an object.
This English pronoun heads an adjective clause. These clauses modify nouns and pronouns.
Relative Pronoun Examples
Here’s a list of relative pronouns in the English language.
- Who is used for a person as a subject.
- Whom refers to a person as an object.
- That refers to a person, thing, or animal.
- Which refers to a non-living thing.
Another relative pronoun you should know is whose. It’s a possessive relative pronoun that shows ownership. There are also compound relative pronouns like the following.
- Whoever.
- Whomever.
- Whichever.
- Whatever.
Relative Pronouns Used in Sentences
Here are some examples of relative pronouns used in sentences.
- Kevin, who is a teacher, should be a good example to these elementary students.
- The car that she was driving was her mother’s.
- The town mayor rewarded the man who saved the boy’s life with lifetime groceries.
- Suzette is the girl whom I was talking about.
- The book, which I got from the bookstore, is sold out.
Reflexive Pronouns
A reflexive pronoun is preceded by adjectives, adverbs, nouns, and pronouns to which they refer. That means the antecedent is located in the same clause. This pronoun is also used as an object, referring to the same thing or object as the subject.
A reflexive pronoun can function as a direct or indirect object. These pronouns in italics show the pronoun’s objective function.
- I rewarded myself with a new phone.
- She taught herself piano lessons.
It can also function as an object of a preposition. For example:
- I went there by myself.
Reflexive Pronoun Examples
A reflexive pronoun is singular if it only refers to one person or object. Here are some examples.
- Myself.
- Yourself.
- Herself.
- Himself.
- Itself.
Plural reflexive pronouns refer to more than one person or thing. Here’s a list of the most commonly used pronouns.
- Themselves.
- Ourselves.
- Yourselves.
You can use themselves or themself as singular gender-neutral pronouns. It’s a substitute for the gender-specific pronouns himself and herself.
Reflexive Pronouns Used in Sentences
Below are examples of reflexive pronouns in sentences. Notice how the pronouns are the objects of the verb or preposition and are the same as the sentence’s subject.
- I walked home all by myself after the party.
- That evening, Rosalie watched herself on the big screen. The premier night was a success.
- They got themselves into a new organization before graduating.
- She gave herself a treat by going to the spa and salon.
- He loves himself enough to tolerate her actions. So he walked away.
- You can’t live all by yourself. You need a dog to help you around.
Intensive Pronouns
In traditional grammar, an intensive or emphatic pronoun is like a reflexive pronoun. However, it has a different function. This type of pronoun only emphasizes the sentence’s antecedent or subject.
Intensive pronouns are usually found right after the noun or pronoun they modify. You might also find them before verbs. A verb refers to a word that shows action, condition, or existence.
A writing tool like Grammarly or ProWritingAid might ask you to remove intensive pronouns to make your writing concise. Grammarians consider these pronouns unnecessary to the sentence because they do not give any new information.
Intensive Pronoun Examples
Here are some examples of the most common intensive pronouns.
- Myself.
- Yourself.
- Himself.
- Herself.
- Itself.
- Ourselves.
- Yourselves.
- Themselves.
The main difference between intensive and reflexive pronouns is that reflexive pronouns reflect onto the subject. Meanwhile, intensive pronouns highlight the subject of the sentence.
Intensive Pronouns Used in Sentences
Here are some intensive pronouns in action.
- The ant itself was able to carry a leaf from the ground.
- You yourself can become a doctor if you continue your studies.
- He himself climbed the mountain to take a photo of nature.
- I myself don’t dare to speak up about the issue.
- The president themselves had shortcomings in the event.
- The team itself is under the supervision of Ms. Darcy.
Indefinite Pronouns

Indefinite pronouns are pronouns that replace unknown nouns. They don’t specifically identify what they are referring to. For example, if you say that someone ate ice cream, we don’t know who did.
Understanding subject-verb agreement using indefinite pronouns takes a bit of practice. You already know that singular pronouns agree with singular verbs, while plural pronouns agree with plural verbs. But which indefinite pronoun is singular or plural?
Indefinite pronouns have three main uses.
- Referring to an unknown person.
- Referring to a whole or absence.
- Referring to a general quantity.
Indefinite pronouns are also closely associated with distributive pronouns. This pronoun disperses a verb’s effects on more than one item or individual at a time. They include each, either, and neither.
Indefinite Pronoun Examples
Listed below are the singular indefinite pronouns. Remember this list, so you don’t use the wrong pronoun in your sentences.
- Nobody.
- Everybody.
- Another.
- Anybody.
- Anyone.
- Each.
- Anything.
- Everyone.
- Everything.
- Little.
- Less.
- Much.
- Nobody.
- No one.
- Nothing.
- One.
- Someone.
- Something.
- Somebody.
Here are some plural indefinite pronouns you should know.
- Few.
- Fewer.
- Both.
- Many.
- Others.
- Several.
Some indefinite pronouns can both be singular and plural. Use either a singular or plural verb.
- All.
- More.
- Any.
- Most.
- Some.
- None.
- Such.
Indefinite Pronouns Used in Sentences
Here are some indefinite pronouns in action.
- Everybody got the question wrong.
- Someone always puts the flag down and keeps it when it rains.
- Anything is possible if you put in enough dedication.
- You can be anybody you want to be if you set achievable goals for your dreams.
- No one has entered the abandoned house since the 1970s.
- Somebody needs to wait outside and look for clues while we’re working.
- Many have tried to approach her. But they all failed.
Demonstrative Pronouns
A demonstrative pronoun is a kind of pronoun that points to specific things or people. It can be used as a subject or object. Here are some examples of demonstrative pronouns in sentences.
- These look nice. (subject).
- I like these. (object).
A common practice in demonstrative pronouns is that nouns follow them. Pronouns with these types of words act as adjectives. Consider the example below.
- This website is crashing.
In this sentence, this functions as an adjective modifying the noun website.
Demonstrative Pronoun Examples
Here’s a list of singular and plural demonstrative pronouns.
- Those is used to point to more than one item from a distance.
- These is used to point to multiple nearby items.
- This is used to point to a single nearby item.
- That is used to point to a single item from a distance.
Demonstrative Pronouns Used in Sentences
Here are some examples of demonstrative pronouns used in sentences.
- Please place those inside the drawer.
- That isn’t mine. Try asking Jane if it’s hers.
- I like this shirt. I should buy this.
- I haven’t seen this in a while.
- That’s okay. We can reschedule the meeting if you’re busy.
- This place used to be my school. (This as a demonstrative adjective modifying place).
- Those books might be relevant to your research. (Those is a demonstrative adjective modifying books).
Interrogative Pronouns

Interrogative pronouns are pronouns that appear in questions, and their antecedents are the answers to these questions. For example, if Tina washed the car, then the antecedent of Who in Who washed the car? is Tina.
This class of pronouns is not considered gendered pronouns like personal pronouns. You’ll find them as the first weird in questions like Who was that? or what color do you like? These common questions also end with a question mark.
Interrogative pronouns can be singular or plural when asking a single question. You’ll find them in direct questions and rhetorical questions but not indirect questions.
Interrogative Pronoun Examples
Here’s a list of interrogative pronouns in English.
- Who and whom refer to persons.
- Whose is used to ask questions about possessions.
- What is for objects and abstract concepts
- Which is for question where there are multiple choices.
Note how why, how, when, and where are not interrogative pronouns. That’s because their antecedents are not nouns but adverbs.
Interrogative Pronouns Used in Sentences
Here are some interrogative pronouns in action.
- Whose notebook is this?
- Whose poem are you reading for the recital?
- Who is the owner of this notebook?
- Who wants to go with me to Gina’s birthday party?
- What animal has four legs and growls?
- Which do you like better, the red scarf or the blue shoes?
- To whom are you giving that lovely scrapbook?
- Whom were you referring to?
- Which among the countries has the best-tasting food?
Reciprocal Pronouns
Countless resources state that reciprocal pronouns indicate that there are two reciprocal pronouns: each other and one another. These pronouns suggest that more than one person is performing an action, both receiving the same effects.
These pronouns are usually easy to use. When referring to two people, the correct pronoun is each other. But multiple people use the pronoun one another.
Reciprocal Pronouns Used in Sentences
Here are some examples of reciprocal pronouns used in sentences.
- Cheerfulness and health beget each other.
- Many people think my sister and I resemble each other.
- We shouldn’t see each other anymore.
- Lyn and Mar corrected each other’s work to prepare for the Science test.
- The community has a strong sense of belongingness because they care for the well-being of one another.
- We should help one another get through these tough times.
- The dogs watched one another with their tails wagging.
What Type of Pronoun is That?
That is either a relative pronoun or a demonstrative pronoun. As a relative pronoun, it is used in restrictive clauses or as a substitute for who and which. The demonstrative pronoun that points to a singular noun from a distance.
What Type of Pronoun is They?
They is a personal pronoun in plural form. The third-person pronoun refers to many persons, places, or things. It’s also in the nominative case, functioning as a subject or predicate nominative. You can also use it as a singular, gender-neutral pronoun.
What Type of Pronoun is It?
It is a third-person pronoun in singular form. It refers to a place, thing, or animal. This pronoun can be in a subjective or objective case.
What Type of Pronoun is This?
This is a demonstrative pronoun. This singular pronoun points to a nearby object.
What Type of Pronoun is Us?
Us is a first-person personal pronoun in plural form. It’s also in the objective form, functioning as a direct object, indirect object, or object of a preposition.
What Type of Pronoun is Them?
Them is a third-person personal pronoun in plural form. It’s also in the objective form, functioning as a direct object, indirect object, or object of a preposition.
What type of Pronoun is She?
She is a third-person personal pronoun that refers to a female person. It’s singular and in the nominative case.
What Type of Pronoun is These?
This is a demonstrative pronoun that points to multiple objects nearby.
Wrapping It All Up
I hope this lesson on pronouns for kids and adults helped you differentiate between their types. Use this part of speech correctly in business, academic, or creative writing.
Remember that pronouns are words that replace nouns or noun phrases. They go beyond the words he, she, it, they, I, we, and other personal pronouns.
Other types of pronouns include relative pronouns, reflexive pronouns, intensive pronouns, indefinite pronouns, etc.

Comments are closed.