Questions are an essential part of English grammar. They can be used to make requests, express interest, or ask for information. In this post, I’ll look at the different types of questions and how to structure them correctly. I’ll also provide some examples to see how they’re used in practice. So, whether you’re new to questions in English or just want a refresher, keep reading for all the essential info!
Why Are There Different Types of Questions?
Different types of questions are structured differently to obtain several categories of information. Yes/no questions are amongst the most common, and they can be answered strictly with yes or no. Question-word questions demand a more informative answer. Choice questions usually provide the person who answers with several options that are included in the question.
What Are the 4 Types of Common Questions?
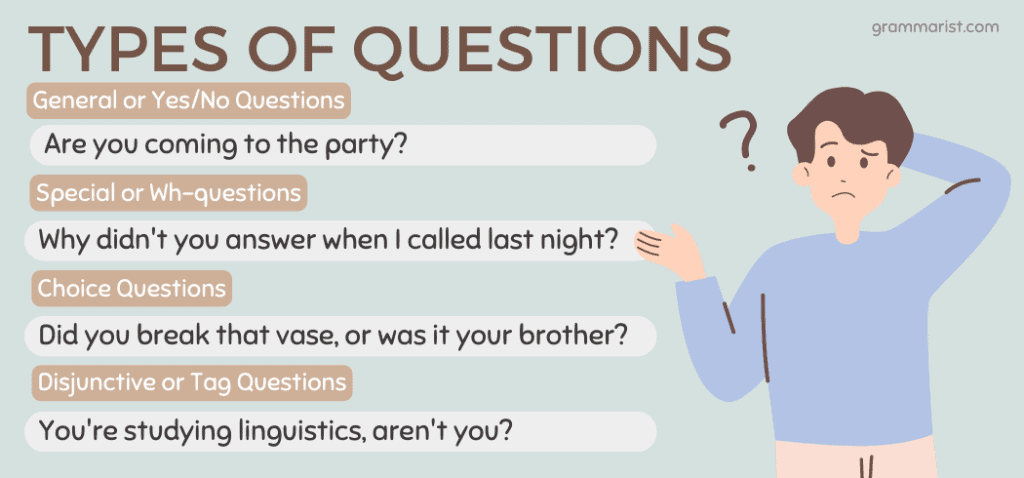
English grammar divides its questions into four main types.
- General or Yes/No Questions
Yes/no questions are typically used to gather information or confirm something already known. For example, you might ask your teacher if the class is canceled tomorrow or whether the exam will be multiple choice.
For example:
- Do we have to turn in the essay this Friday?
- Are you coming to the party?
- Does Jenna like to listen to Coldplay?
On the other hand, general questions usually require a longer answer. These are typically used to explain something in more detail, such as how to complete a task or what they think about a particular topic.
Asking follow-up questions is also a good way to clarify something that was said earlier. Choosing the right question based on the information you’re trying to obtain is important.
- Special or Wh-questions
Special or wh-questions use a specific word at the beginning. These words include why, what, where, who, when, which, and how.
Examples:
- Why didn’t you answer when I called last night?
- What books are we supposed to read for the upcoming test?
- Where did Yara leave my car keys?
- Who was that person at the restaurant with you?
- When is the next big festival?
- Which color is your favorite?
- How do you plan to pay for everything?
- Choice Questions
Choice questions allow the respondent to select one of several possible responses. They are composed of two components, and the conjunction is used to connect the two of them. They are also known as closed questions or multiple-choice questions.
Questions based on options can either be broad and open-ended or more narrowly focused on a particular topic. If the topic of the sentence is not at the heart of the question being asked, a comprehensive response is required.
For example, if you ask someone, “Do you like salted snacks or sweet treats?” the center of this question is what they prefer, not who prefers it. The answer would be, “I like salted snacks.”
Choice question examples:
- Do you like rock music or EDM?
- What color would you choose between blue and green?
- Is he a client, or does he work here?
- Did you break that vase, or was it your brother?
- Disjunctive or Tag Questions
This question category is made up of two parts. A tag question is usually a statement followed by a mini-question. The mini-question typically uses an auxiliary verb, such as “are” or “do,” and aims to confirm the statement’s truth.
For example, “You’re studying linguistics” would be followed by the tag question, “aren’t you?” In this case, the speaker is assuming that the person they are speaking to is studying linguistics, and they are asking for confirmation.
Tag questions are typically used in spoken English, adding interactivity and immediacy to a conversation. However, they can also be used in written English for rhetorical effect.
For example, a character in one of my novels might say something like, “I didn’t kill him, did I?” This type of tag question indicates that the character is doubting their innocence, and it creates suspense for the reader.
What Are the 7 Question Words in English?

We use seven main words in English grammar to form questions: how, what, why, who, which, where, and when.
How Do You List Questions?
If you have to list several questions in a sentence, there are multiple ways to do so.
Without Using Question Marks
You don’t have to use question marks when listing questions in a sentence. You should, however, separate the questions using commas. For example:
- I wanted to know how you felt about the whole situation, your thoughts, and what would you have done differently.
Using Numbers
When you have a long series of questions to enumerate in a single sentence, consider adding numbers in parentheses before each one.
For example:
- Part of the research was to identify (1) what percentage of shoppers are likely to make an impulse buy, (2) what are the most common products people buy on impulse, and (3) how much people spend on impulse purchases.
Using Colons
Another way to list questions is to use colons when introducing them and separate them using commas.
Example:
- I want to know three things: how do I apply for a loan, how much money can the bank give me, and what interest I’ll have to pay in total.
How Do You Form Questions in English Grammar?
If you want to turn a sentence into a question, change the order of the words and add a question mark. Direct questions typically start with a verb followed by a subject.
Examples:
- I am smart. > Am I smart?
- The dog is playing. > Is the dog playing?
- Sarah is wide awake. > Is Sarah wide awake?
- I love ice cream. > Do I love ice cream?
When you have a question word, always start your questions with it.
Examples:
- Who are you talking to?
- When does the next bus come?
- Why does George never pay attention in class?
When you have modal verbs, start your question with these.
Examples:
- Could you pass me the orange juice?
- Should you be working this late at night?
- Might I bother you for a glass of water?
Simple Question Example
- Yes/No Questions
Here are some examples of basic yes/no English questions:
- Did you hear that Gilly has a new boyfriend?
- Can you please bring me my phone charger?
- Did Lucas go to the gym this morning?
- Will you finish your homework before dinner?
- Is it possible to learn a whole new language in a month?
- Are you coming with me to the wedding this weekend?
- Wh-questions
Here are some examples of wh-questions:
- What would you like to order for supper?
- Why do bunnies sleep with their eyes fully open?
- Who is this person next to you in the picture, grandma?
- Which sweater should I wear with my green leather pants?
- Where do you plan to go on vacation next year?
- When do you think would be the best day to call you back?
- Indirect Questions
Indirect questions are formal questions that we employ when looking to be polite.
Suppose you need directions to find a certain place. You wouldn’t just stop a stranger and ask them, “Where’s the pet shop?”
Instead, you would say, “Could you tell me where the pet shop is?”
Here are some examples of indirection questions:
- Would you mind telling me your name?
- Do you know where I could find this restaurant?
- Do you have any idea what time the bank closes?
- Would it be possible to take a paint sample with me?
- Tag Questions
Here are some examples of tag questions:
- Farah can speak French, can’t she?
- You don’t know anything about that, do you?
- I’m not an annoying person, am I?
- You won’t return his phone calls, will you?
- She wouldn’t mind helping me with my project, would she?
- You’re majoring in Women’s Studies, aren’t you?
- Negative Questions for Confirmations
It’s common to form negative questions in English when you’re looking to confirm a thought or a suspicion. Here are some examples of these kinds of questions:
- Didn’t you have classes early in the morning? (I suspect you had classes.)
- Shouldn’t you avoid drinking coffee on an empty stomach?
- Wouldn’t you be better off ending this toxic relationship?
The Bottom Line
English grammar divides basic question types into four main categories: general or yes/no questions, special or wh-questions, choice questions, and disjunctive or tag questions. To form a question in English grammar, change the order of the words and add a question mark at the end. Questions typically start with a verb followed by a subject. When you have a question word (e.g., who), always start your question with it.
