The simple present is a most straightforward English grammar concept. It’s used to describe a current or continuous action, but there are a few rules to know first. I’ll cover the present simple tense, see how it’s formed, and take a look at some present simple examples that I whipped up for you.
What Does Simple Present Tense Mean?
The simple present tense is really just a verb tense that indicates an action is currently happening or is regularly occurring. You can use the verb as it is or add suffixes like “-e” or “-es’” based on some simple rules.
The simple present tense is usually used with the adverbs always, never, and sometimes. It’s a simple concept once you get the hang of it, so I’ll break it down further for you.
How Do We Form Present Simple?
Usually, the present simple tense is formed by taking the root form of the verb as it is or, depending on the person, by adding -s or -es at the end.
For example, the simple present tense of “walk” is “walks.”
To form a standard sentence in the simple present tense, you need a subject and a verb. The subject can be a noun or even a pronoun, and the verb must agree with the subject in number (singular or plural). For example:
- I walk to school every day.
- You never listen to me.
- He always eats pizza on Fridays.
- We sometimes play games after school.
- They always watch TV on Saturday mornings.
What Are the Rules of Present Simple?
There are a few simple present tense rules I always remember. First, use the base form of the verb. This means that you don’t need to add “-s” or “-es” to the end of regular verbs in the present simple.
For example, you would say “I walk to school” instead of “I walks to school.”
You only need to add one of these suffixes if the subject is he, she, or it.
So, you would say “She walks to school,” not “It walks to school.”
Second, make sure your verbs agree with your subjects. If you have a plural subject, you must use a plural verb form.
For example, you would say “They walk to school,” not “They walks to school.”
What Is Simple Present Tense Formula?
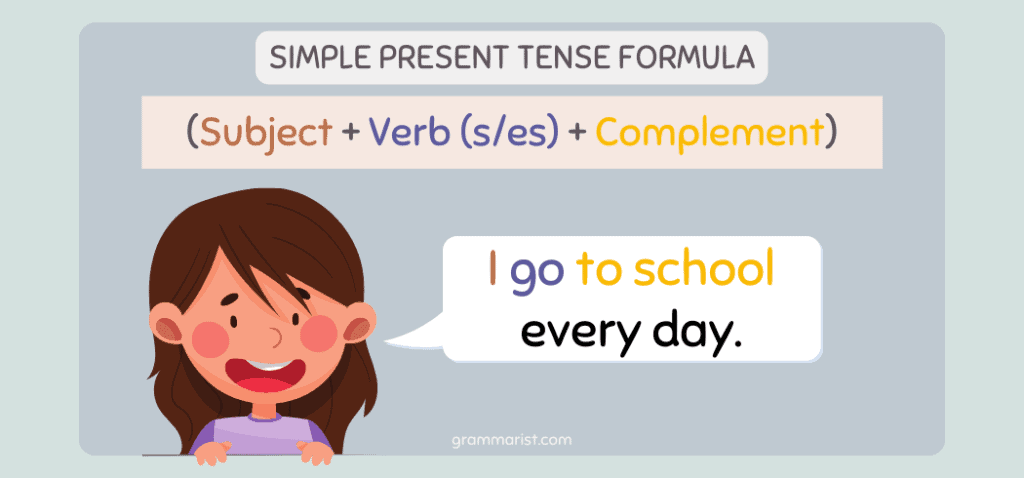
I’ve got a formula for the simple present tense that will help you remember more easily: (Subject + Verb + Complement) or (Subject + Verb). Boom!
Verbs in the simple present tense are always in the base form, which means they don’t change no matter if the subject used is singular or plural. To make a sentence sound more formal, I would add “s” or “es” to the end of the verb. Make sense?
For example:
- He plays tennis. (base form)
- She writes a letter. (base form)
- They live in New York. (base form)
What Are Three Forms of Present Simple?
There are three ways to form the present simple tense in English grammar.
The first method is by using the present form of the verb. This works with “I” and “you” pronouns and for plural subjects.
Examples:
- I go to school every day.
- They know all about Britain’s history.
The second way of forming present simple is by adding the “-s” termination to a verb. This only works when the subject of the sentence is singular.
Examples:
- Maria knows how to talk to children.
- Tony deals with these things daily.
For the third form, just add “-es” at the end of the verb. The rule is that the subject has to be singular, and the verb needs to end in o, x, z, ss, ch, th, gh, or sh.
Examples:
- He dashed to help her with the groceries. (from the verb “to dash”)
- She relaxes every day after work. (from the verb “to relax”)
Examples of Using Simple Present Tense

In English, the simple present tense describes habits, unchanging situations, general truths, and things that happen regularly. For example, I would use the simple present to say, “I walk to school every day.”
We also use the simple present to describe how often something happens with adverbs of frequency like always, usually, often, sometimes, and never.
For example, “I never miss a day of school.”
The simple present can also describe future events that are scheduled or planned. For example, “My plane leaves at 6:00 PM.”
Other present simple examples:
- The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.
- Tons of people wake up every day and go to school or work.
- At night, they eat dinner and go to bed.
Simple Present Question Examples
Asking a question in the present simple, you need to use the auxiliary verb “do.”
For example, if you wanted to ask someone their name, you would say, “Do you have a name?”
To form a question, you simply take the statement form of the present simple and add the auxiliary verb do before the subject.
For example, “I am eating breakfast” becomes “Do you eat breakfast?”. Easy, right?
If there’s already an auxiliary verb used in the sentence, such as in the case of “She is singing a song,” you would simply move that auxiliary verb to before the subject, so the question becomes, “Is she singing a song?”
Simple Present Negative Examples
To make the simple present negative, add “do not” or “don’t” before the verb.
For example, to make the sentence “I eat breakfast every day” negative, you would say “I don’t eat breakfast every day.”
You can also use contractions like “don’t” and “doesn’t” to make negative sentences.
For instance, the negative form of “She eats breakfast every day” would be “She doesn’t eat breakfast every day.”
Final Thoughts
The rules of the present simple are pretty straightforward. In short, you use the present simple when you want to talk about habits or permanent situations. The present simple is a basic verb tense in English used to indicate habitual or regular actions. To form or use the present simple, we start with the base form of the verb (the infinitive without “to”). I hope my guide helped you better understand the concept!