The verb tense in the English language tells us when an action or condition occurs. We use them to communicate our messages.
My handy guide will focus on the key differences between the present perfect and simple past tense. Become a self-professed grammar geek as I teach you when to use each verb tense and how to form them.
What is the Present Perfect Tense?
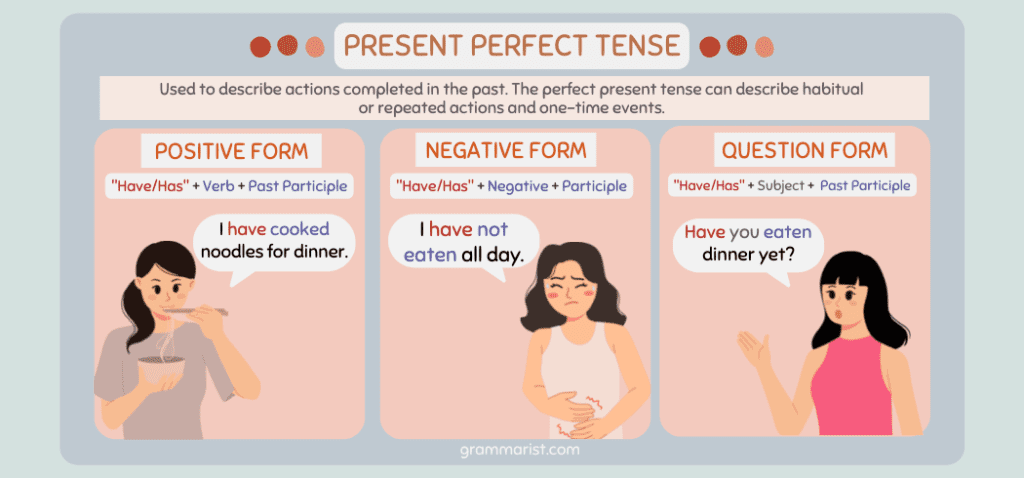
In English grammar, the present perfect tense is a verb tense used for actions that took place recently or at an unspecified time.
I would form the present perfect tense by using the auxiliary verb has or have and the past participle of the verb. Some examples include have done, has delivered, and has seen.
For the helping verb, use has if the subject is singular. Use have if the subject is plural.
Here, I’ll show you an example:
- I have tried reading these English books a few times after seeing their positive book reviews.
Remember that not all past participles end in -ed. Irregular verbs often change in spelling or don’t change at all. For example, sink becomes sunken and become stays the same. Here’s a short list of common irregular verbs and their past participle forms.
- Say – said.
- Make – made.
- Go – gone.
- Take – taken.
- Be – been.
What is the Simple Past Tense?
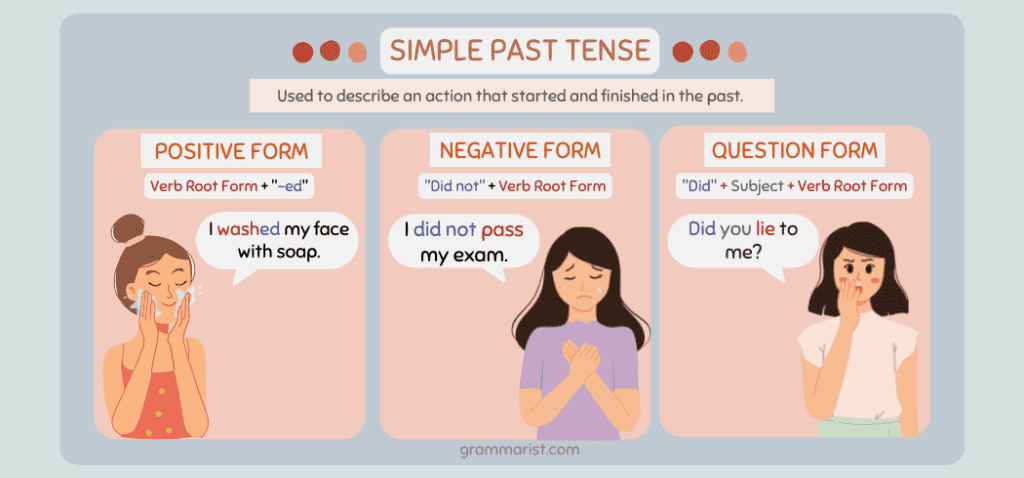
I use the simple past tense for a finished action at a definite time.
For regular verbs, we express an action during a finished time by adding -d or -ed at the end of the main verb. Some examples include danced, talked, and lied.
But irregular verbs have no single pattern for their verb forms. For example, eat becomes ate and drink becomes drank. For example:
- I ate an entire pie yesterday morning.
- I sent him an email yesterday.
Difference Between Simple and Past and Present Perfect Tense
The main difference between the simple present and past simple tenses are the time reference. One verb tense shows the completion of an action at an unknown time, while the other is known. One may also show action in the past at an unfinished time.
When to Use Present Perfect Tense
The perfect aspect looks at a specific time and refers to these actions that occurred up to that relevant time.
I would use the present perfect tense for unfinished actions or a historical event that started in the past and continues until now. That means we can use it for ongoing events. For example:
- I have seen Jera twice this lunch time.
The present perfect tense is also ideal for actions or situations in the past when we don’t know the exact time they happened. For example:
- I have read that book recently.
Another tip to learning when to use this verb tense is when you see common adverbs of duration that answer, “how long?”. Some keywords include for and since, which indicate the time frame, such as since yesterday. For example:
- I have lived in this subdivision for six years.
- I have known Sean since we were kids.
The negative adverb never also requires the present perfect tense. For example:
- The teacher has never sent the lessons by email.
A present perfect question is presented this way.
- Have you included the reference list in our research paper?
But in informal questions, you can remove the auxiliary verb have. Here is an example of an unusual question asked by Joker to his victims.
- You ever danced with the devil in the pale moonlight?
When to Use Simple Past Tense
Simple past verb tenses are used when the time period has finished. Some time expressions to use with the simple past tense include yesterday, last week/month/year, three days ago, etc. For example:
- I saw the old pillow last week.
I’ve also seen the simple past tense used when giving older information when the time is clear. For example:
- I met Cece in 2005 when we were kids.
You can use the simple past tense with for when the action is already done. For example:
- We became friends for five years. (We’re not friends anymore)
There’s also a distinction in their verb conjugations. You might notice that the simple past tense uses a single verb, while the present perfect tense requires an auxiliary verb and the past participle verb.
Below are examples of sentences that use simple verbs for simple past tense.
- We went to the museum yesterday.
- The guests had a good day yesterday.
- The men visited the shops yesterday.
When expressing questions in the simple past tense, start your questions with did and use the base form of the verb. For example:
- Did you take a bath a while ago?
Remember that the simple past tense is not used to show a sequence of events.
Simple Past vs. Present Perfect Tense Summary
English learners should differentiate between verb tenses to form grammatically accurate sentences. This guide has shown you the difference between the simple past and present perfect tense.
The present perfect tense is for actions that occurred in a time period that is not yet done. You can also use this tense for actions that occurred at indefinite times. Meanwhile, the simple past tense is for an event where the time period has been finished.