What’s your favorite song? One of mine is The Glorious Sons’ Pink Motel. The previous sentence is a fact about me and shows how to use possessive pronouns.
Possessive pronouns in English grammar are pronouns that replace nouns while showing possession.
This grammar guide about possessive pronouns for kids and adults will answer all your questions on the topic. Learn its definition with a list of all the possessive pronouns. You’ll also discover the rules on its correct usage and how it differs from a possessive adjective.
Then, you can answer the helpful pronoun worksheets I provided once you’ve finished reading the article and absorbing everything I have to share.
What Is a Possessive Pronoun?
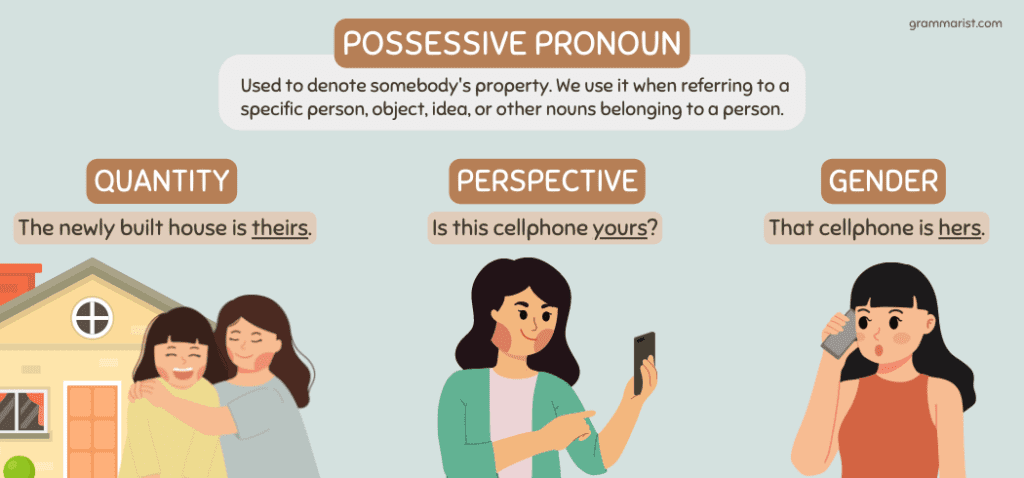
A possessive or absolute possessive pronoun is used to denote somebody’s property. We use it when referring to a specific person, object, idea, or other nouns belonging to a person.
The use of the correct possessive pronoun depends on three things:
- Quantity (e.g., its for singular, theirs for plural)
- Perspective (e.g., mine for the first person, yours for the second person)
- Gender (e.g., his for male, hers for female)
There are several other types of pronouns in the English language, such as interrogative pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns.
Possessive Pronouns List
Here’s a complete chart of possessive pronouns in English.
Singular
Person: 1st person
Gender: Male, female, gender-neutral
Possessive Pronoun: Mine
Person: 2nd person
Gender: Male, female, gender-neutral
Possessive Pronoun: Yours
Person: 3rd person
Gender: Male
Possessive Pronoun: His
Person: 3rd person
Gender: Female
Possessive Pronoun: Hers
Person: 3rd person
Gender: Gender-neutral
Possessive Pronoun: Theirs
Plural
Person: 1st person
Gender: Male, female, gender-neutral
Possessive Pronoun: Ours
Person: 2nd person
Gender: Male, female, gender-neutral
Possessive Pronoun: Yours
Person: 3rd person
Gender: Male, female, gender-neutral
Possessive Pronoun: Theirs
Here, I whipped up some examples of possessive pronouns in a sentence.
- Is this bag yours?
Here, the speaker asks whether the other person owns the bag. The possessive pronoun yours is a 2nd person singular pronoun. The antecedent here is the singular noun your bag. Make sense?
- Mine is the perfect grammar tool with complete lessons. (Mine as a 1st person singular pronoun)
- Her artwork and yours are the best ones I’ve seen in the gallery. (Yours as a 2nd person singular pronoun)
- That phone is his. (His as a 3rd person, male, singular pronoun)
- The necklace was hers before you were born. (Hers as a 3rd person, female, singular pronoun)
- Mo is a fantastic musician. The piece you listened to a while ago is theirs. (Theirs as a 3rd person, gender-neutral, singular pronoun)
- The baby is ours. (Ours as a 1st person plural pronoun)
- Everyone in this room deserves to be heard. The decision is yours to make. (Yours as a 2nd person plural pronoun)
- The group visited yesterday, so the documents left on the table are probably theirs. (Theirs as a 3rd person plural pronoun)
How to Use Possessive Pronouns
The rules for using possessive pronouns are easier than you think, trust me. All you have to do is treat them as nouns since they are a type of possessive noun. If you always keep that in mind, you’ll remember how to use possessive pronouns.
Determining the Antecedent
A possessive pronoun is a type of possessive noun that is simplified to make the sentence more concise. It indicates the noun’s possession of another noun by replacing the entire word or phrase. Consider the sentence below.
- Original sentence: My eyeglasses are broken. Her eyeglasses are in perfect condition.
Simplified sentence: My eyeglasses are broken. Hers are in perfect condition.
In this sentence, the possessive pronoun hers is used to avoid repetition. After all, the purpose of pronouns is to avoid redundancy.
Although not explicitly stated, context clues will tell us that the antecedent of hers is her eyeglasses.
Here are more sample sentences.
- I forgot to bring a calculator. Can I borrow yours? (Yours as a replacement for your calculator)
- The flower shop across the market is hers. (Hers as a replacement for her flower shop)
- Her template is fun and creative, but mine is straightforward and formal. (Mine as a replacement for my template)
- The siblings left a few minutes ago. I think those grocery bags are theirs. (Theirs as a replacement for their grocery bags)
- His is the land he tills. (His as a replacement for his land)
Avoid writing unclear sentences where the possessive pronoun’s antecedent cannot be determined. For example:
- Unclear sentence: I was looking for hers. (Her what?)
Clear sentence: I didn’t look for your cardigan. I was looking for hers.
Although the second sentence doesn’t specifically say it, the context shows that hers refers to her cardigan.
Possessive Pronouns as Subject or Object
Because a possessive pronoun replaces a noun, we can use it as a subject or object.
For example:
- My slippers are red. Yours are blue. (Yours as a subject)
- I found Jia’s lost gadget. I can’t locate yours. (Yours as an object)
- Ours is a finite earth. (Ours as a subject)
- You can find my hiding spot behind hers. (Hers as an object)
Remember that a subject pronoun is the doer of the action. Take a peek at these possessive pronoun examples.
- Kurt received his test scores today. Mine isn’t released yet.
- The documents and laptop on the table are mine.
In the first sentence, mine functions as the subject of the sentence since it represents what the sentence is about. Although it is not mentioned, the antecedent of mine is my test scores.
The second sentence uses mine as a subject complement. A subject complement identifies or represents the subject. One trick to identifying the subject complement is to look for a linking verb before it.
The object pronoun is the receiver of the action or another object. Here are some examples of objective possessive pronouns in sentences.
- I do not like my hairstyle. But I love yours.
- The dogs are covered in mud. I gave mine a bath.
- Miguel and I are neighbors. My house is located across his.
In the first sentence, yours functions as a direct object because it receives the action love. That means your hairstyle is loved by the speaker.
The second sentence uses mine as an indirect object. Indirect objects are the receiver of the direct object in the sentence. That means mine (or my dog) was given a bath.
Possessive pronouns can also be objects of prepositions. In the third sentence, his functions as the object of the preposition across. Its antecedent is his house.
The complete prepositional phrase is across his (across his house), which modifies the action verb located.
Subject-Verb Agreement Using Possessive Pronouns
It can be challenging to practice subject-verb agreement when the subject is a possessive pronoun. For example, while ours is plural, the following verb can be singular.
That’s because the verb form is not based on the number of owners. It’s based on the number of people or things being talked about. Check out the pair of sentences below.
- Incorrect: Your recipes taste good. Mine is too sour.
- Correct: Your recipes taste good. Mine are too sour.
The first sentence is incorrect because “is” is not the appropriate verb. The antecedent of mine is my recipes and not my recipe. Since “recipes” is plural, the verb form should be are.
Here’s another example.
- What’s your favorite ice cream flavor? Hers are chocolate and cookie dough.
The verb are is used correctly despite the singular possessive pronoun because hers refers to her favorite ice cream flavors, which are chocolate and cookie dough. Flavors agrees with are and not is.
Mastering subject-verb agreements with possessive pronouns requires a clear understanding of the pronoun’s antecedent. Always make it clear what noun or noun phrase is referred to by the possessive pronoun.
Possessive Pronouns vs. Possessive Adjectives

Sometimes, adjectives may look like pronouns. Demonstrative adjectives look like demonstrative pronouns, and indefinite adjectives look like indefinite pronouns. The same is true with possessive adjectives resembling possessive pronouns.
While a possessive pronoun replaces a noun or noun phrase, a possessive adjective modifies a noun or noun phrase. For example:
- I like my coffee white.
- The white coffee is mine.
In the first sentence, my is a possessive adjective, modifying the noun coffee. But in the second sentence, mine is a possessive pronoun that refers to my white coffee.
Here’s a list of possessive adjectives and their corresponding possessive pronouns.
| Possessive Adjective | Possessive Pronoun |
| My | Mine |
| Your | Yours |
| Our | Ours |
| Its | Its |
| His | His |
| Her | Hers |
| Their | Theirs |
Like possessive pronouns, possessive adjectives can also avoid repetition and redundancy in sentences. Analyze the difference between the two sentences below.
- Candace is proud of Candace’s perfectly baked cookies.
It sounds weird to mention my name twice in the sentence. To avoid awkwardness, use a possessive adjective to modify perfectly baked cookies.
- Candace is proud of her perfectly baked cookies.
Since possessive adjectives are not nouns or pronouns, they cannot function as subjects or objects. For example:
- She read her newspaper today.
- The newspaper she read is hers.
Her newspaper is the direct object of the first sentence. However, her cannot stand alone as an object because it is a possessive adjective. In the second sentence, the possessive pronoun hers functions as a subject complement because it represents her newspaper.
Like most adjectives, possessive adjectives come before the nouns they modify. Consider the sentence example below.
- My mother is the best chef I know.
The possessive adjective my comes before the noun it modifies, which is mother.
Below are more sentence examples where the possessive adjective comes before the noun it modifies.
- That bag contains her most important documents and cards.
- His bookshelf consists of the classics and new romance novels.
- The band played our favorite song while you were gone.
- I sold my old van to a friend.
- Their school hymn sounds like ours.
The Possessive Pronoun His
His is one of the two possessive pronouns that can also be adjectives. Its function depends on its usage and placement in the sentence. For example:
- His poem was short and sweet. (His as a possessive adjective)
- That poem is his. (His as a possessive pronoun)
When we use his as a subject, subject complement, direct object, indirect object, or object of the preposition, then it’s a possessive pronoun. For example:
- His was the best song I heard at the concert last night. (His as a subject)
- Out of all the movie recommendations, I enjoyed his the most. (His as a direct object)
- The cats are adorable, especially John’s. I gave his a pat on the head. (His as an indirect object)
- Lucas and I are neighbors. My house is beside his. (His as an object of the preposition beside)
When we use his as a possessive adjective, it comes before the noun or noun phrase it modifies. For example:
- His frown turned into a smile when he saw Janet. (His modifies frown)
- I enjoy going to his parties all the time. (His modifies parties)
- I gave Michael the necklace of his mother. (His modifies mother)
The Possessive Pronoun Its
Like his, its also functions as a possessive pronoun or possessive adjective. Its function depends on its usage and placement in the sentence. For example:
- The bird is injured. Its wings are broken. (Its as a possessive adjective)
- We have a pet bird. If you find loose feathers, it’s its. (Its as a possessive pronoun)
When we use its as a subject, subject complement, direct object, indirect object, or object of the preposition, then it’s a possessive pronoun. For example:
- Our Golden Retriever is outside. The entire yard is its. (Its as a subject complement)
- This tree’s leaves are darker than the other trees’ leaves. I fancy its the most. (Its as a direct object)
As a possessive adjective, its comes before the noun or noun phrase it modifies. For example:
- Its leaves are falling because of the season. (Its modifies leaves)
- Your document is visually appealing. I like its font style. (Its modifies font style)
Improper Usage
Now that you know the rules for using these pronouns, let’s look at the possessive pronoun mistakes to avoid.
Using Possessive Pronouns as Modifiers
You already know that pronouns such as personal and possessive pronouns take the place of nouns and noun phrases. Therefore, they may function as subjects and objects but never as modifiers.
Do not use possessive pronouns as adjectives, adverbs, or other forms of modifiers. For example:
- Incorrect: Mine Science teacher asked me a question about plant cells.
- Correct: My Science teacher asked me a question about plant cells.
Mine is a possessive pronoun. Therefore, it cannot modify the noun Science teacher. It can only replace my science teacher. The correct word to use instead of mine is my.
Here are more examples of incorrect and correct uses of possessive pronouns in sentences.
- Incorrect: This is my pillow, and that is yours pillow.
- Correct: This is my pillow, and that is your pillow.
- Correct: This is my pillow, and that is yours.
- Incorrect: Her room was as big as hers study room.
- Correct: Her room was as big as her study room.
- Incorrect: Theirs dinner was memorable.
- Correct: Their dinner was memorable.
- Correct: Theirs was memorable. (However, this sentence is unclear because of the lacking antecedent.)
Referring to the Owner for Subject-Verb Agreement
It’s a general rule that every pronoun must agree with the noun or noun phrase it stands for. The sentence’s subject is not the owner, but the owner’s possession.
Make sure to analyze the antecedent of the possessive pronoun to determine the correct verb form to use. For example:
- Incorrect: The Smiths’ house is large, but theirs are enormous.
- Correct: The Smiths’ house is large, but theirs is enormous.
Based on context, we can conclude that the speaker is comparing whose house is bigger. Therefore, theirs stands for their house. We use is in the second clausebecause we are referring to one house instead of multiple houses.
Below are more sample sentences.
- Incorrect: He couldn’t remember which tickets was his.
- Correct: He couldn’t remember which tickets were his.
- Incorrect: The building down the street are ours.
- Correct: The building down the street is ours.
- Incorrect: Your eyes are round. Mine is small.
- Correct: Your eyes are round. Mine are small.
Its vs. It’s
Another mistake is the use of apostrophes in possessive pronouns and adjectives. It’s vs. its is a very common confusion among English writers, especially when using its as a possessive adjective. For example:
- Incorrect: The dog’s color is unique. It’s fur has three shades of brown.
- Correct: The dog’s color is unique. Its fur has three shades of brown.
One of the reasons for this mistake is the idea that we use an apostrophe and s (‘s) to show possession. But this rule only applies to possessive nouns. We can write dog’s fur, but we can’t write it’s fur.
Remember that it’s is a contraction of it is. For example:
- The dog is adorable. It’s a Golden Retriever.
We also don’t use an apostrophe for other possessive pronouns, such as yours, ours, theirs, his, and hers. For example:
- Incorrect: That hotel room is her’s.
- Correct: That hotel room is hers.
- Incorrect: The locker you’re trying to open is hi’s.
- Correct: The locker you’re trying to open is his.
- Incorrect: This reward is your’s because you’ve been an obedient student since the first day.
- Correct: This reward is yours because you’ve been an obedient student since the first day.
- Incorrect: Our’s is a damaged but repairable culture.
- Correct: Ours is a damaged but repairable culture.
- Incorrect: There was a big group of high school students at the table next to their’s.
- Correct: There was a big group of high school students at the table next to theirs.
Tips for Using Possessive Pronouns
I have a few tips for using possessive pronouns you should follow to avoid grammatical errors.
First, apostrophes should never cross your mind. Remember that the apostrophe and s rule only applies to possessive nouns. Ours, yours, his, hers, its, and theirs already show possession without taking apostrophes.
Next, check the placement of the possessive pronoun. Remember that pronouns replace nouns and noun phrases, so you won’t find them before another noun. These pronouns can stand on their own without modifying another noun.
Lastly, read your sentences aloud. Doing so will help you identify whether the sentence sounds correct or not. It will also help you pinpoint which part is incorrect.
For example, when you use a possessive adjective instead of a pronoun, you’ll be able to catch the mistake when you read it out loud.
What Is a Gender-Neutral and Nonbinary Pronoun?
A gender-neutral pronoun is a pronoun that does not specify a person or animal’s gender. We use it to be more sensitive to someone’s gender identity and expression.
The purpose of using gender-neutral language is to promote inclusivity. It helps us prevent using words that may be interpreted as discriminatory, biased, or demeaning. We also don’t want to imply that a specific name, activity, or position is attributed to one sex.
The singular use of they and other derivative forms emerged in the 14th century but was not accepted by prescriptive commentators. Today, it is recognized as a gender-neutral pronoun by the American Dialect Society, Merriam-Webster, and several style guides.
The possessive theirs isn’t only a plural pronoun. It’s now also a singular, gender-neutral, or non-binary alternative to gender-specific pronouns.
Instead of using gendered pronouns his and hers or his/hers when we don’t know someone’s gender identity, we can use theirs. For example:
- Incorrect: I saw the receptionist sitting on that chair yesterday. That pen must be his/hers.
- Correct: I saw the receptionist sitting on that chair yesterday. That pen must be theirs.
You can use the gender-neutral pronoun when someone’s gender doesn’t need to be specified in the context. For example:
- Incorrect: A doctor should administer the anesthesia. That job is his.
- Correct: A doctor should administer the anesthesia. That job is theirs.
It’s also the best option when referring to someone who identifies as non-binary. For example:
- Incorrect: Kitty is beautiful. I’ve never seen eyes as shiny as hers.
- Correct: Kitty is beautiful. I’ve never seen eyes as shiny as theirs.
Is Yours Singular or Plural?
The possessive pronoun can be singular or plural. The quantity depends on the number of people you refers to. For example:
- Happy holidays, April! This Christmas gift is yours.
In this sentence, yours refers to Christmas gift. It is singular because both April is singular.
Here’s another example.
- Good morning, Mom and Dad! I believe these letters are yours.
The speaker refers to two people in the sentence, Mom and Dad. Therefore, yours is plural as it refers to your letters or Mom and Dad’s letters.
Can I Use Theirs as a Singular Possessive Pronoun?
Yes, you can use theirs as a singular possessive pronoun. Use it to show gender neutrality or when referring to a person who identifies as non-binary. For example:
- Mia said the package is theirs.
Its other derivative forms, them, they, their, and themselves can also be used as singular pronouns.
Is Our a Pronoun?
Traditional grammar states that our is a possessive adjective, not a possessive pronoun. Its pronoun counterpart is ours. For example:
- Byron and I are expecting our first baby.
Our is an adjective because it modifies first baby.
Here’s an example of ours in a sentence.
- There’s no love sweeter than ours.
Ours is a possessive pronoun because it replaces the noun phrase our love.
Final Word on Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are used to show someone’s or something’s property of any noun or noun phrase. The seven possessive pronouns in the English language are mine, ours, yours, its, theirs, his, and hers.
I hope these grammar notes helped you understand the definition and use of possessive pronouns. If you’re ready for a quiz, try answering the exercises below.