Possessive pronouns may seem identical at first glance to adjectives. But there’s a vast difference between the two. Like other pronouns, possessive pronouns replace nouns. And like other adjectives, possessive adjectives modify nouns.
Keep reading to learn the difference between possessive pronouns and adjectives. Then, answer the worksheet provided.
Possessive Pronouns vs. Possessive Adjectives Chart
Below is a list of possessive pronouns and their corresponding possessive adjectives.
Subject/Antecedent
I (First person, singular)
Possessive Adjective
My
Possessive Pronoun
Mine
Subject/Antecedent
You (Second person, singular or plural)
Possessive Adjective
Your
Possessive Pronoun
Yours
Subject/Antecedent
He (Third person, singular, male)
Possessive Adjective
His
Possessive Pronoun
His
Subject/Antecedent
She (Third person, singular, female)
Possessive Adjective
Her
Possessive Pronoun
Hers
Subject/Antecedent
It (Third person, singular)
Possessive Adjective
Its
Possessive Pronoun
Its
Subject/Antecedent
We (First person, plural)
Possessive Adjective
Our
Possessive Pronoun
Ours
Subject/Antecedent
They (Third person, singular or plural)
Possessive Adjective
Their
Possessive Pronoun
Theirs
Possessive Pronouns
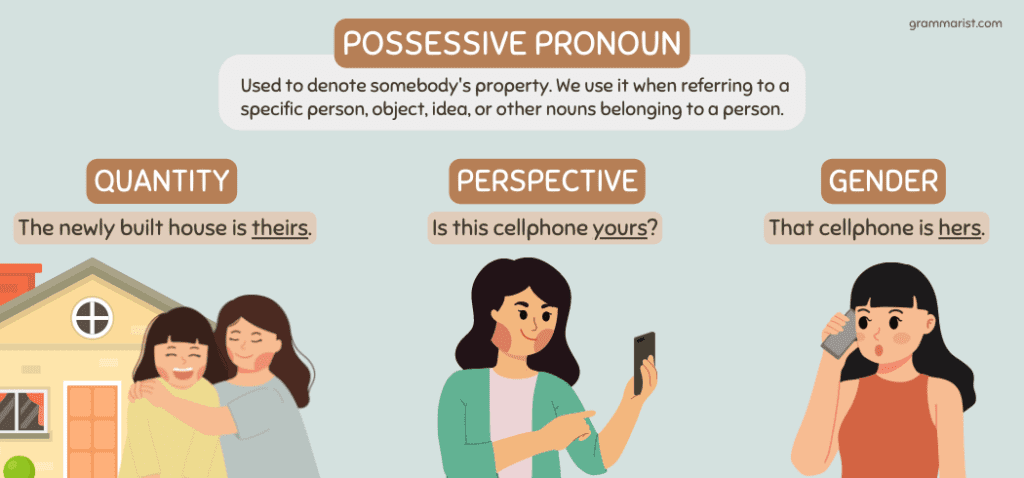
Possessive pronouns are a type of possessive noun that simplifies the construction of a possessive adjective and a noun. For example, instead of saying my dog repetitively, you can say mine.
- That dog is my dog.
- That dog is mine.
Here are more examples of possessive pronouns in action.
- Your flowers are red, while her flowers are blue.
- Your flowers are red, while hers are blue.
- He has a beautiful smile. That smile is his.
- Ours was an amazing love story.
Possessive Adjectives

Possessive adjectives, also known as possessive determiners, modify nouns and noun equivalents by showing possession. Like possessive pronouns, they also avoid repetitions in sentences. For example:
- Patricia loves Patricia’s outfits.
- Patricia loves her outfits.
Instead of saying the noun Patricia twice, we say her before the noun outfits to avoid making it sound awkward.
A common mistake among English speakers is that they classify possessive adjectives as possessive pronouns. However, words like my, your, and her cannot replace nouns in sentences.
One of the main rules when using possessive adjectives is that they are always followed by a noun. My phone, her sister, and our dog are some examples. Here are some sentence examples.
- Your breakfast is ready.
- A snake sheds its skin four to twelve times a year.
- We are in charge of our own futures.
Another common mistake when using possessive adjectives is saying it’s instead of its. It’s with the apostrophe is a contraction for it is. For example:
- Incorrect: The cat is adorable. It’s fur is black.
- Correct: The cat is adorable. Its fur is black.
Their and Theirs
We usually use they, them, their, theirs, and themselves as third-person plural pronouns. However, we can also use it as a singular pronoun or adjective when referring to someone who is non-binary.
We also use this pronoun if we do not know whether to use he or she as the pronoun for a general subject.
Final Word on Possessive Pronouns and Possessive Adjectives
Now you know the difference between possessive pronouns and possessive adjectives. Both parts of speech show ownership, but their placements and functions in sentences differ.
Remember that possessive pronouns replace possessive adjectives and the noun they modify, while possessive adjectives modify nouns.