The English language groups grammatical nouns as either singular or plural. That means there are either one or multiple persons, places, objects, events, or animals.
Did you know that there’s more than one rule on how to make a word plural? In my little guide, I’ll show you the two types of plural nouns, their rules, and a list of examples. I also provided a worksheet that will test your understanding of plural nouns.
What Is a Plural Noun?
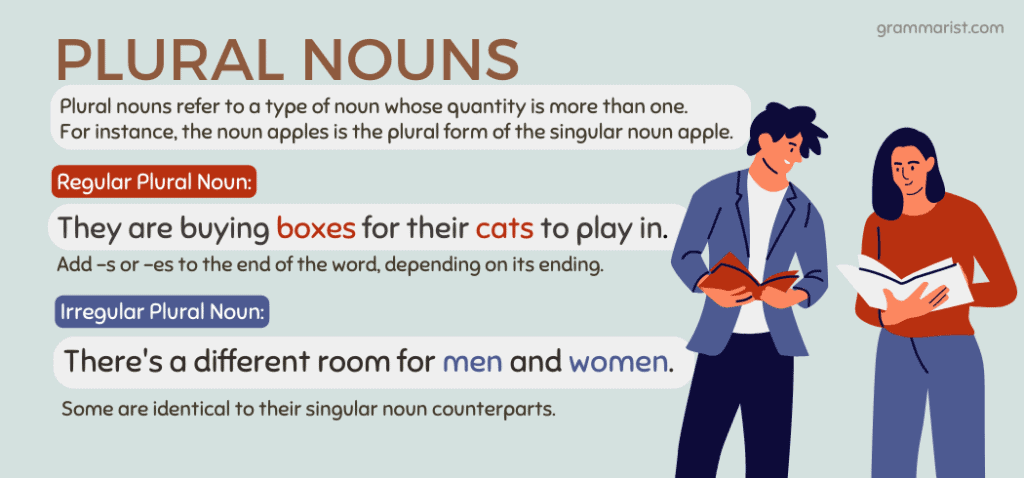
While singular-form nouns refer to one person, place, object, or event, plural nouns refer to a type of noun whose quantity is more than one.
For instance, the noun apples is the plural form of the singular noun apple. It means there can be two or more apples. The same is true with the noun buses, which is the plural form of the singular noun bus. The plural form of the singular noun bug is the noun bugs.
I live in Eastern Canada, and one of our well-known animals is a moose. I am always puzzled over what the plural of it is. Mooses? Meese? The answer is actually just moose. There are some exceptions to plural nouns like this.
But here are more plural noun examples that make sense.
- Film – films
- Baby – babies
- Ox – oxen
Remember: mass nouns, non-count nouns, or uncountable nouns do not have plural forms. For example:
- Food
- Air
- Advice
- Blood
- Research
Plural Nouns vs. Singular Nouns
Singular nouns represent a single quantity of any noun. It can be a person, place, event, object, or animal. For example:
- One dress
- A strand of hair
- This daisy
- The towel
Plural nouns refer to something whose quantity is more than one. For example:
- Five dresses
- Two strands of hair
- Those daisies
- The towels
Plural Nouns vs. Possessive Nouns
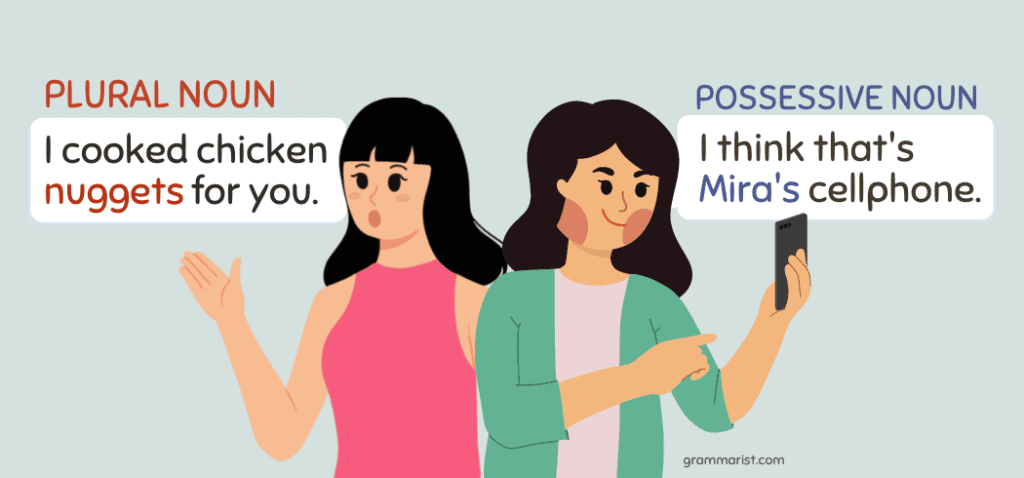
Possessive nouns are one of the types of nouns that show ownership. Like plural nouns, they end in s. However, possessive nouns always have an apostrophe (‘) before the s. Consider this example:
- The lamp’s bulb.
Here, lamp’s refer to the possession of lamp instead of multiple lamps. The lamp has a bulb.
Here are more examples of possessive nouns.
- Rose’s artwork
- Mira’s phone
- The lion’s tail
Plural nouns do not have possessive forms unless they are possessive plural nouns. For example:
- Bosses
- Tails
- Nuggets
- Jackets
- Jackets’ pockets (possessive plural noun)
- Students’ books (possessive plural noun)
Plural Nouns vs. Collective Nouns
Unlike plural nouns, collective nouns represent groups of people, things, or animals. For instance, a school of fish represents a group of fish as a united whole. Here are more examples of collective nouns.
- A pair (of shoes)
- A pack (of cards)
- A pride (of lions)
- A class (of students)
Notice how these collective nouns are treated as singular nouns. If we say pairs of shoes, we refer to more than a pair.
What Is a Regular Plural Noun?
Regular nouns are nouns that follow the typical pattern of making them plural.
There are simple rules for making regular nouns plural. We either add -s or -es to the end of the word, depending on its ending. Sometimes, we also change the last letter of the word before adding -s.
Add -s to the end of a word when making it plural. For example:
- Cat – cats
- Dog – dogs
- Idea – ideas
Add -es to the end of a word if its singular form ends in -s, -ss, -ch, -x, -sh, -o, or -z. For example:
- Bus – buses
- Lass – lasses
- Bush – bushes
- Crutch – crutches
- Box – boxes
- Blitz – blitzes
- Mango – mangoes
A few words, such as photos, pianos, and halos, are exceptions.
The plural noun form may require you to double the -s or -z before adding -es. For example:
- Fez – fezzes
If the regular noun ends in -f, fe, change it to ve, then add -s. For example:
- Wife – wives
- Knife – knives
Another regular plural noun rule is to change -y into -ies. For example:
- City – cities
- Puppy – puppies
But if the letter before -y is a vowel, just add an -s. For example:
- Ray – rays
- Toy – toys
Singular nouns that end in -us will change into -i for their plural forms. For example:
- Cactus – cacti
Change the word into -es if the singular noun ends in -is. For example:
- Analysis – analyses
- Parenthesis – parentheses
If the singular noun ends in -on, change it into -a. For example:
- Phenomenon – phenomena
Check out this list of regular plural nouns.
- Boss – bosses
- Baby – babies
- Candy – candies
- Gift – gifts
- Curry – curries
- Cat – cats
- Day – days
- Collection – collections
- Movie – movies
- Tray – trays
- Shoe – shoes
What Is an Irregular Plural Noun?
Irregular noun rules are inconsistent because they follow no specific guidelines. For example, the irregular plural noun form of child is children, and goose’s plural form is geese. Here are more examples.
- Man – men
- Foot – feet
- Mouse – mice
- Person – people
Another tip when using irregular nouns is recognizing that some are identical to their singular noun counterparts. They can be troublesome nouns because it takes memorization to identify these words. Here are some examples:
- Fish – fish
- Moose – moose
- Species – species
- Sheep – sheep
- Deer – deer
Below is a list of irregular plural nouns.
- Woman – women
- Aircraft – aircraft
- Moose – moose
- Means – means
- Trout – trout
- Swine – swine
- Salmon – salmon
- Spacecraft – spacecraft
- Series – series
- Louse – lice
- Penny – pence
- Caveman – cavemen
- Policeman – policemen
- Alumna – alumnae
- Formula – formulae
- Index – indices
- Appendix – appendices
- Vertex – vertices
- Axis – axes
- Addendum – addenda
- Datum – data
- Forum – fora
- Genus – genera
- Stylus – styli
Summarizing English Plural Nouns
This article has taught you the plural nouns’ definition. This type of noun refers to more than one person, animal, place, idea, animal, or thing.
Remember that the plural form of nouns depends on their singular noun versions. For example, toy becomes toys, but knife becomes knives. Louse becomes lice, and sheep stays the same.