What happens when you mix the perfect and continuous verb tenses? Great question! The past perfect continuous tense is one of the most complex verb tenses that use had been with the present participle form of the verb.
When writing, I use this to express actions that occurred for a duration of time in the past and ended before another time in the past. Keep reading to learn the uses and forms of the past perfect continuous tense with sentence examples.
What is the Past Perfect Continuous Tense?
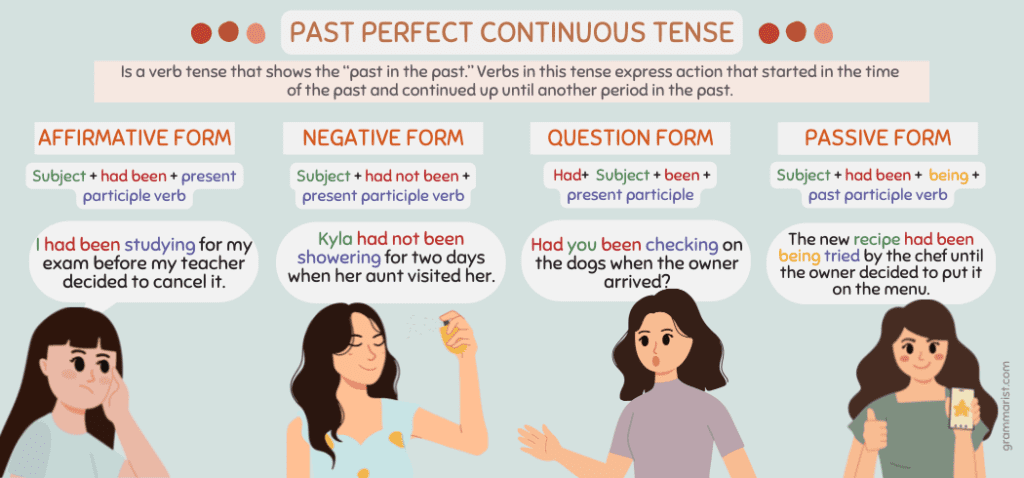
In English grammar, the past perfect continuous or past perfect progressive tense is a verb tense that shows the “past in the past.” Verbs in this tense express action that started in the time of the past and continued up until another period in the past.
Here are some past perfect continuous examples.
- We had been speaking to her for an hour before Linda came.
- Had she been studying a new language before she moved abroad?
- I was exhausted because I had been jogging.
Unlike other continuous tenses, the past perfect continuous tense uses the auxiliary verb had been.
When to Use Past Perfect Continuous Tense
I sometimes find it tricky to use because the past perfect continuous tense has many uses and rules. Let’s take a look at each of them together.
A Period in the Past Before Another Past Event
The past perfect progressive tense describes temporary situations that occurred over a period of time in the past before another period in the past. We usually use it with the simple past form. Here’s an example in a sentence:
- I had been calling James for two hours, and I was tired.
In this sentence, had been calling is in the past perfect progressive tense. It happened before another period in the past, which is I was tired. Here are more examples:
- I had been meeting her for two days when my mom finally messaged.
- Jake had been taking the stairs until the workers fixed the elevator.
- Conan had been drinking tea ever since he found it could prevent diseases.
Aside from when, other conjunctions or adverbs of time we use to show the time limit or the end of durations of time include since, until, and before.
Cause of Something in the Past
We may also use the past perfect continuous tense when showing cause and effect in the past. Here, the cause happened for a duration of time in the past. The effect also happened in the past. Take a look at this example.
- She felt tired because she had been running errands the whole week.
In this sentence, the effect is she felt tired, which is in the simple past form. The cause is she had been running errands the whole week, which is in the past perfect continuous form.
Here are more examples:
- She graduated Summa Cum Laude because she had been getting high test scores and had been attending extra-curricular activities
- Mary and Jonah lost weight because they had been attending Pilates classes.
- Our yard got destroyed because it had been raining hard.
Past Perfect Continuous Forms
Remember that the past perfect continuous form expresses an action that started in the past at a definitive time. Then, it continued for a duration of time until another point in the past. Here’s the formula for the past perfect continuous form.
Affirmative Form
The most typical form of the past perfect continuous sentence is its affirmative or positive form. Here is the correct sentence structure to use:
- Subject + had been + present participle verb.
For example:
- The dancer had been preparing for the performance for two months before he switched to a new genre.
- The chef had been trying this new recipe until the owner decided to put it on the menu.
Negative Form
Negative sentences always include the word not. Here’s the correct structure for the negative form of past perfect continuous tense.
- Subject + had not been + present participle form of the verb.
Here are some examples.
- I had not been reviewing my notes for two weeks when the teacher announced a surprise quiz.
- Kyla had not been showering for two days when her aunt visited her.
- My seatmate had not been attending classes often when the event happened.
Interrogative Form
Question sentences always have question marks. If you’re asking a question in the past perfect continuous tense, follow this formula:
- Had + subject + been + present participle.
For example:
- Had you been checking on the dogs when the owner arrived?
- Had Amy been liking Christopher for two weeks when he asked to marry Joanna?
You can also use not when asking negative questions. For example:
- Had the boss not been speaking for a while when the new clients showed up?
Passive Form
Passive forms always emphasize the action rather than the doer of the action. In this type of sentence, the subject is not the doer of the action. Here’s the correct structure for the passive form of the past perfect continuous tense.
- Subject + had been + being + past participle verb
Here are some sentence examples.
- The performance had been being prepared by the dancer for two months before he switched to a new genre.
- The new recipe had been being tried by the chef until the owner decided to put it on the menu.
You can also change the second clause into passive form. For example:
- The new recipe had been being tried by the chef until it was included on the menu by the owner.
Contraction With Past Perfect Continuous

You can contract the subject and the first auxiliary verb when using the past perfect progressive tense. Here are some suggestions you can try in informal writing.
- I had been – I’d been.
- You had been – You’d been.
- He had been – He’d been.
- She had been – She’d been.
- It had been – It’d been.
- We had been – We’d been.
- They had been – They’d been.
Take a look at these examples.
- I’d been seeing him for months when I found out he was taken.
- You had been on a diet since last month when the doctor asked you to eat more.
You can also contract had with the word not for negative sentences. For example:
- I hadn’t been changing my phone case until my old one accumulated a stain.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense and Stative Verbs
Like other continuous verb tenses, do not use the past perfect continuous tense with stative verbs/non-continuous verbs/mixed verbs. Only use it with action verbs or dynamic verbs.
Adverb Placement
You can use adverbs like always, only, never, just, etc. in this verb tense. Here’s an example showing the placement of grammar adverbs.
- I had only been waiting for two minutes when Jens entered the room.
Past Continuous vs. Past Perfect Continuous
The past continuous tense is a verb tense that expresses an ongoing action in the past until another event in the past happened. It’s like the past perfect continuous but without including time durations like for five minutes or since Thursday.
We form past continuous verbs using the verb’s was/were + present participle form. For example:
- I was exercising when Jiro called me.
Meanwhile, the past perfect continuous emphasizes the durations of time. Its verb form is had been + present participle form. For example:
- I had been exercising for ten minutes when Jiro called me.
Past Perfect Simple vs. Past Perfect Continuous
The past perfect simple is used to emphasize the completion of an event. The correct form of this tense is had + past participle verb. For example:
- The engineer had met with the homeowner when the architect came.
Meanwhile, the past perfect progressive tense focuses on the activity’s duration in the past. Its verb form is had been + present participle form. For example:
- The engineer had been meeting with the homeowner for two weeks when he decided to hire a new architect.
Final Word on Past Perfect Continuous Tense
I hope this past perfect continuous tense lesson helps you achieve perfect grammar. It’s one of the 12 verb tenses that expresses “the past in the past.” I know it sounds confusing at first, but it’s a simple concept once you understand it.
Use the basic structure of the past perfect continuous tense had been + present participle. Only use it when the duration of time in the past is emphasized. Otherwise, use the past perfect or past continuous tense.