The past continuous tense is one of the many English tenses used to express a progressive or ongoing action that happened in the past. You see it used all the time in popular fiction books. You can use it as affirmative, negative, and question sentences.
Find out the different uses and forms of the past continuous tense as I lay it all out for you. Then, challenge yourself to a downloadable exercise I made.
What Does Past Continuous Mean?
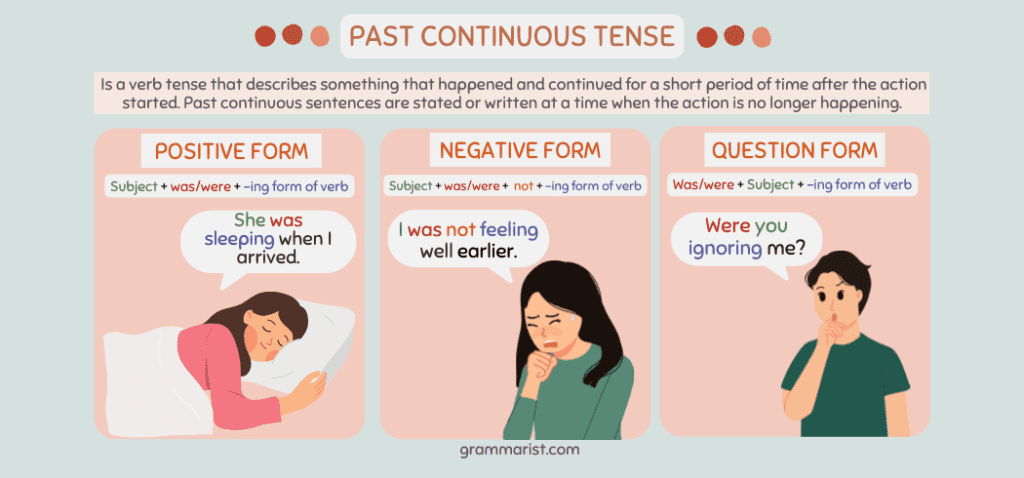
In English grammar, the past continuous or past progressive tense is a verb tense that describes something that happened and continued for a short period of time after the action started. This is actually the tense I use most when I’m writing.
Past continuous sentences are stated or written at a time when the action is no longer happening. We may also use it to indicate a background situation or temporary situation when the main action begins.
Consider this sentence in the past continuous form below.
- The wolf was howling when the Johnsons arrived at the cabin yesterday evening.
Continuous actions are at the core of the past progressive tense. Above, you’ll notice that the act of howling was happening when the Johnsons arrived. But the event might not be happening anymore.
Past Continuous Forms
The past continuous form comes in more than one formula. The positive form is established from the past tense of “to be,” the main verb, and the “-ing” ending of the verb’s simple form. In other words, past continuous verbs use this formula.
- Subject + was/were + -ing form of the verb.
Negative verb forms follow this formula.
- Subject + was/were + not + -ing form of the verb.
Follow this formula if you’re using question forms in the past continuous tense.
- Was/were + subject +-ing form of the verb.
Note the difference between past continuous and other English tenses. The past perfect form uses the past participle form of the verb instead of the present participle.
Past continuous tense is also different from the simple tense. Simple past tense only uses the -d or -ed form of the verb.
Rules for Past Continuous Tense
Remember that the past continuous tense describes an instantaneous action or action in progress in the past.
Habitual Action in the Past
You can use the past continuous tense to talk about actions repeated in the past, using time expressions “constantly” and “always” to show the precise time. Remember that the placement for grammar adverbs is between “was/were” and the action verb.
For example:
- He was always running and strength training.
- My father was constantly talking about his dream car.
Simple Past Tense for Shorter Action, Past Continuous for Longer Action
We use the past continuous tense for two ongoing actions in the past. One usually shows interruption in time or happens alongside the other. That means you can use it to talk about unfinished actions in the past.
Use the simple past tense for the shorter action, and the past continuous tense for the longer action to show parallel actions. Here’s an example of a correct sentence.
- I was baking cookies when you went home a while ago.
Examples of Past Continuous in Sentences

Take a look at these past continuous tense examples I whipped up to help you better understand how to use it. These complete sentences show the different uses of the verb tense and are in the form of negative sentences, positive sentences, and question sentences.
- I was reading an email newsletter when Jonah messaged me.
- I was not sleeping when the lady visited.
- Last Saturday, I was working when the police stopped by my neighbor’s house.
- Were you ringing me when I went to the mall?
What is the Past Continuous of Go?
The past continuous form of “go” is “was going” or “were going,” depending on the subject.
Learn the Other Verb Tenses
English tenses appear in different verb forms. The past continuous tense uses “was/were” and the -ing form of the verb.
Use the past continuous or progressive tense to show two ongoing events in the past. It can indicate a past habitual action, or an earlier event interrupted by another situation.
What other verb tenses do you wish to learn?