Modal verbs of possibility, modals of possibility, or possibility modal verbs express the likelihood of a situation happening. They include may, might, could, must, and have to.
I’ll show you the definition of modals of possibility, their proper sentence structures, and examples of how to use them. Then, you can answer the worksheet I made to test your understanding of the topic. Ready?
What Are Possibility Modals?
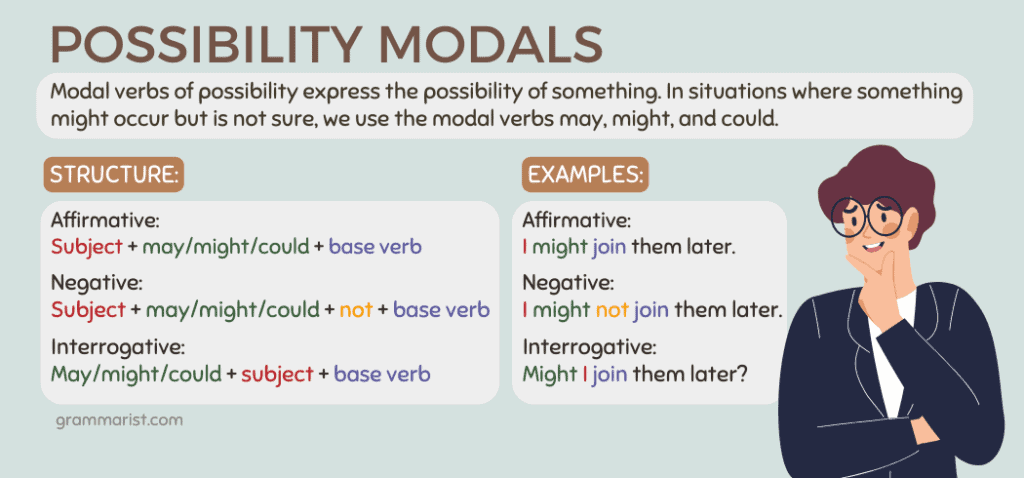
While some modals express intent, ability, or necessity, modal verbs of possibility express the possibility of something. In situations where something might occur but is not sure, we use the modal verbs may, might, and could. Basically, anything that expresses a future possibility.
The main rule for using modal verbs of possibility is to follow this structure:
- Affirmative: subject + may/might/could + base verb
- Negative: subject + may/might/could + not + base verb
- Interrogative: may/might/could + subject + base verb
For example:
- Affirmative: I might join them later.
- Negative: I might not join them later.
- Interrogative: Might I join them later?
May
Use the modal verb may when showing possibility in the future or present. This verb is more common in formal texts. For example:
- Where is Charles? He may be in another city.
In this sentence I have here, the complete verb may be is in its present simple form.
Here’s another example.
- I may see him later.
This sentence, with may see as the verb phrase, is in simple present form.
Might
The modal verb might also shows possibility in the present or future. But it’s more common in informal conversations. Here are some sentence examples.
- Simple present: Where is Charles? He might be in another city.
- Simple future: I might see him later.
Could
Could is another modal verb that shows an option. It also shows the speaker is not very certain of the possibility. For example:
- Simple present: Where is Charles? He could be in another city.
- Simple future: I could see him later.
Must
A less common modal verb of possibility is must, which shows certainty from the speaker. For example:
- Harry saw his father today. He must be happy.
Have To
Like must, have/has to is a modal verb of possibility that shows certainty from the speaker. For example:
- Winston studied the whole day. He has to be tired.
Modal Verbs of Past Possibility
Aside from showing future and present possibilities, modal verbs sometimes show past possibilities using this structure:
- Modal verb + have + past participle form of the verb
For example:
- Everyone must have been devastated by the bad news.
- Brian could have been at school.
- Your sister may have gone home early.
- The team must have won the tournament.
You Could Always Learn More!
There are several modals in the English language. But the main modals of possibility are may, might, could, must, and have to. They either show certainty or uncertainty of the possibility in the past, present, or future.
Practice using modals of possibility in your sentences. Doing so will help you become a better English speaker and writer.