Do you ever wonder when to properly use “as” and when to use “like?” They sound similar, but they have different meanings. And often, they get lost in translation when moving from speech to formal writing. I’ve seen it happen so many times, especially with new writers. In my guide, I’ll discuss the difference between these two words and give some examples so you can learn to use them properly.
As vs. Like

In English grammar and more formal writing, the word “like” is almost often employed as a preposition to explain how, where, or when the action described by the noun in the phrase is taking place. The basic grammar rule is that the word “as” is a conjunction that joins two clauses together.
When to Use As
The best way to remember the proper usage in sentences for “as” is to think about whether or not you’re trying to join two clauses in the English language.
Examples:
- You’re as pretty as I remember.
- You don’t have to cook much food as I won’t be joining you for dinner.
When to Use Like
“Like” is used to compare two things, but is usually followed by a noun or a pronoun.
Examples with a direct comparison:
- These lights are bright, like the sun.
- I want to go on a safari, but I’m scared of animals like lions and tigers.
- This new ice cream is like the old one but sweeter.
When to Use Like Instead of As
We often use “like” to compare two things or two people.
For example:
- You look just like my sister.
- This new bar is like the one on 5th Avenue.
In this situation, it would be wrong to use “as.” The sentences would sound something like this:
- You look just as my sister.
- This new bar is as the one on 5th Avenue.
The last two sentences are very clearly incorrect.
When to Use As Instead of Like
We use “as” in sentences where it could be replaced with “the way.”
For example:
- You treated him as you should.
- You treated him the way you should.
Like and As a Metaphor
The words “like” and “as” are common figures of speech used to describe similarities between two different things. These seemingly innocuous words can have a powerful impact, lending depth and nuance to our writing.
For example, when taken literally, the phrase “as fast as lightning” suggests lightning moves at a certain speed. But by using these words as metaphors, we can get at a more abstract idea – that lightning moves quickly and without warning.
Similarly, comparing an angry person to a raging storm adds emotional intensity to our writing and conveys the sense that their anger is uncontrolled and chaotic.
Thus, we can see that “like” and “as” are much more than simple connectors; they are valuable tools for evoking vivid imagery in our writing and giving it greater emotional power. In short, these small words have immense expressive potential, making them an invaluable part of any writer’s toolbox.
Should I Use Like or As If?
You want to use “like” before a noun or a pronoun. “As” or “as if” are usually followed by a subject and a verb.
Let’s look at some examples:
- I love the new Givenchy perfume. It smells like cotton candy.
- She keeps repeating the same things as if I don’t know them already.
What Does Not Use Like or As?
Avoid using “like” or “as” when talking or writing in metaphors.
A metaphor is a literary device often used to express ideas or experiences in vivid and memorable ways. Specifically, it describes one thing by referring to another similar thing, using language suggesting the two things are connected in some way.
For example, if you wanted to say that someone was “strong as an ox,” you would use a metaphor to describe their physical strength by drawing an analogy with the legendary strength of this animal.
Metaphors can be used greatly in poetry and other forms of literature, allowing writers to create vivid imagery and use colorful language to engage readers and better convey their message.
Here are some metaphors that don’t use the words “like” or “as”:
- You have the memory of an elephant.
- I’m an early bird.
In the first example, we want to say someone has a really good memory, but we don’t use a simile and say, “you have good memory like an elephant.”
A metaphor is a word or statement saying one thing IS like another thing.
Can We Use As and Like Together?
There are always exceptions when breaking grammar rules, but you can’t use “like” and “as” together. But one can replace the other to convey the same thought if you change the structure of a sentence.
Let’s exemplify:
- You smell as good as a rose does.
- You smell good, like a rose.
Notice how these sentences express the same thought, but we had to change their structure depending on whether we used “like” or “as.”
Like vs. As – Simple Rules to Know
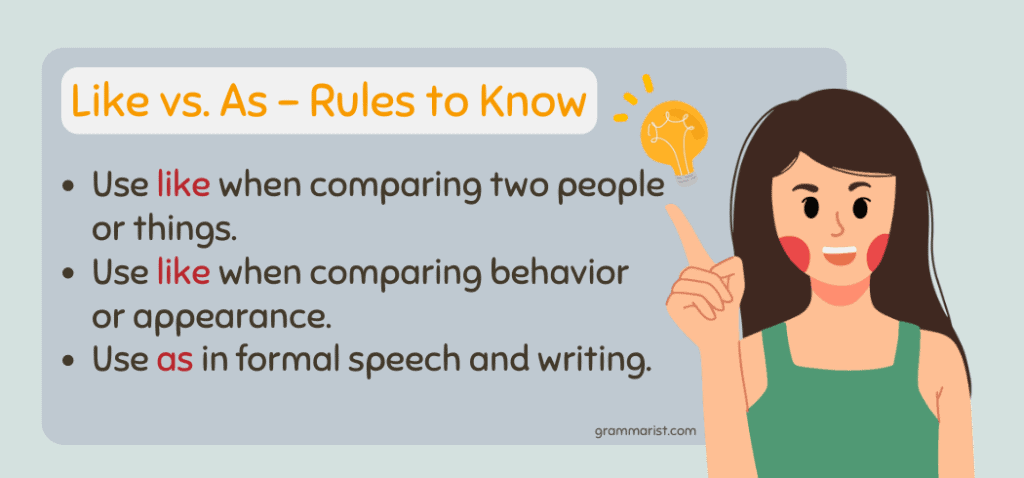
While seemingly similar, “as” and “like” have two different meanings.
Here are some basic rules to keep in mind:
- Use like when comparing two people or things.
- Use like when comparing behavior or appearance.
- Use as in formal speech and writing.
Other Uses of the Word As
There are other instances where the word “as” can fit into speech and writing.
As a Connecting Word
“As” can be used to connect two ideas or sentences. For instance:
- Everything happened as you said it would.
- Leave the table as it is. I’ll clean it up later.
When Talking About a Job or Function
“As” is also employed when discussing a job or a function. For example:
- As president, his main focus was to create more jobs and decrease unemployment.
- As CEO, you are responsible for ensuring people are happy with their jobs.
When Paired with an Adjective
You can also use “as” paired with an adjective. Here are some examples:
- You are as beautiful as I imagined.
- As entertaining as this is, I have to get going.
Other Uses of the Word Like
The word “like” also has more than one use, so let’s look at other situations where you might encounter it.
When Giving Examples
A common use for the word “like” is when giving examples. Here is how to use it:
- Chamomile tea can be bitter, but you can sweeten it with something like sugar or honey.
- Why can’t you be more like your sister?
As a Preposition
When using “like” as a preposition, it’s usually followed by a noun. For example:
- I am nothing like my sister.
- You smell like roses.
As a Verb
Perhaps the most common use for the word “like” is in its verb form. For instance:
- Would they like to join us for dinner?
- I like strawberries best out of all fruits.
The Bottom Line
Once you consistently look at examples, knowing when to use “as” and “like” becomes pretty natural. “As” is commonly employed when joining two clauses, while “like” is used as a preposition with a noun or a pronoun. Now, practice what I taught you with my handy worksheet!