If the English language were a summer blockbuster, then grammar would be the superhero, and usage would be the trusty sidekick. They work together to fight language chaos, yet, like all great duos, they’re very different from one another.
As a writer, author and editor for over a decade now, I’ve seen many people mix up what grammar and usage really are. And, while they seem like different words for the same thing, I promise they’re not, and it’s important to understand that. So, I’ll break down the important details about grammar and usage right here.
What Is Usage in English?
Usage refers to the way our language is used by people who speak or write it when one word, phrase or sentence structure is preferred over others. Think of it as the set of unwritten rules, the street smarts of the English language, if you will. It’s like the cool kid who doesn’t necessarily play by the established rules but somehow manages to sound good doing it.
What Is Grammar?
So many people think grammar and usage are the same thing. But grammar is the straight-laced, rule-abiding citizen of the language world. It’s the structural rules that oversee the configuration of sentences and words in any given language.
Grammar is the reason why “I goes to school” makes English teachers cringe, while “I go to school” gets a nod of approval. With grammar, we set the framework that helps us understand how words and their parts combine to make meaningful sentences.
So, how does it compare to usage? Stick with me; I’ll throw them together and show you.
Differences Between Usage and Grammar
Okay, I want to break this down as simply as possible. Think of grammar as the rule book and usage as the playbook.
While grammar lays out sentence construction’s dos and don’ts, usage takes those rules and adds a layer of real-world application. Usage navigates the nuances of language, slang, regional dialects and colloquialisms that make English rich and vibrant.
But grammar is more black-and-white—it’s about right or wrong. If grammar was a hard set of rules, usage would be the loopholes.
Some Common Usage Examples
Allow me to explain with some visual examples to see what I’m trying to get at.
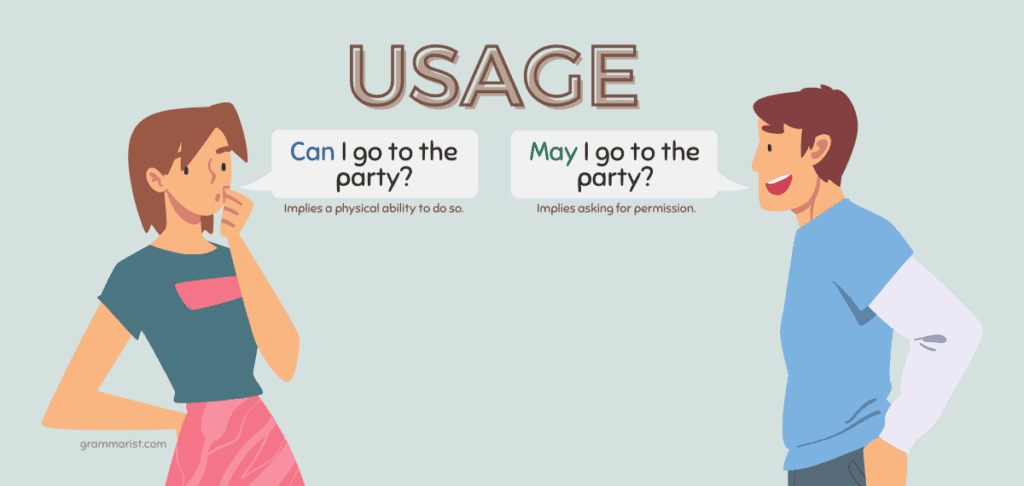
- “Can I go to the party?” This sentence, while perfectly grammatically correct, isn’t ideal when you’re seeking permission. The preferred usage is “May I go to the party?” This is because can implies a physical ability to do so, and may implies asking for permission.
- “I feel bad” vs. “I feel badly.” According to standard usage, “I feel bad” is the right choice. “I feel badly” would mean your sense of touch isn’t working correctly—quite a different meaning, right?
Examples of Bad Word Usage
Sometimes, the misuse of a word can lead to hilariously wrong sentences. Here are a few examples to laugh at.
- “My sister’s husband’s ex-wife’s cousin is my ex-husband.” Here, poor usage of possessives makes the family tree sound like a knotted mess. Instead, I’d say something like, “My ex-husband is distantly related to my brother-in-law.”
- “I literally died laughing.” Unless you’re a ghost typing this, you’re likely misusing the word literally, which pretty much every millennial and younger does these days.
Improper vs. Good Word Usage
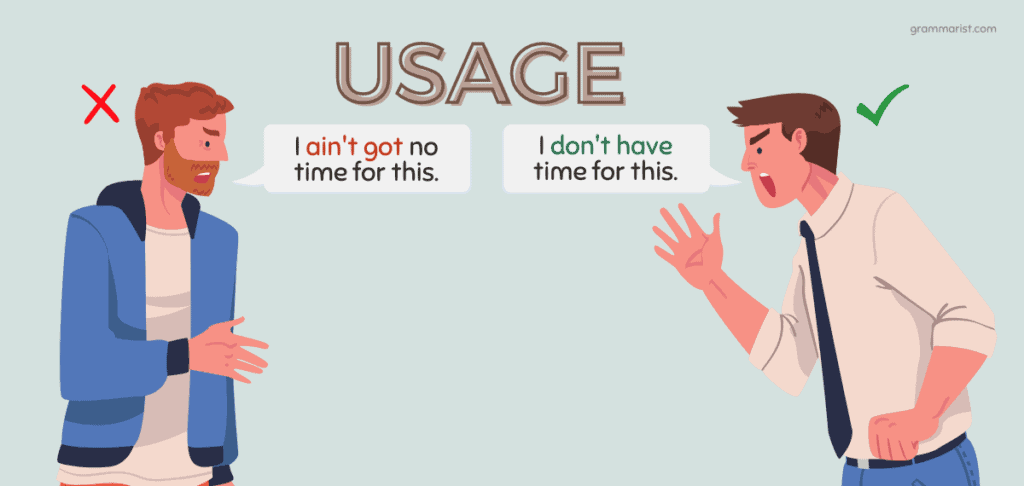
With improper usage, you can confuse readers or listeners and obscure your intended message. For instance:
- Improper: “She done good on her tests.”
- Proper: “She did well on her tests.”
- Improper: “I ain’t got no candy.”
- Proper: “I don’t have any candy.”
Tips for Using Grammar and Usage the Right Way
- Always proofread your work. Look for any grammatical errors and ensure you’re using words correctly.
- Learn the rules of grammar, but also pay attention to how people actually use language.
- Whenever you’re unsure, just consult a dictionary or style guide.
- Take advantage of helpful programs like Grammarly and ProWritingAid to help find grammar and usage inconsistencies in your writing.
Rules About Usage
While usage can be more fluid and nuanced than grammar, it does have a few rules you should think about.
- Always keep your audience in mind: Using slang or regional dialects might not be appropriate in all contexts. Like the word wank; it has entirely different meanings in the UK and the US.
- Try to be consistent whenever possible: If you choose a particular usage style, stick with it throughout your text.
The Bottom Line
So, there’s your crash course on grammar, usage and the fine line that distinguishes them. Though different, these two facets of language work hand in hand to shape how we communicate.
With a solid understanding of both, you’ll be a dominator of language in no time. Keep learning, keep practicing, and most importantly, have fun with it because language is a playground!
List of Usage Examples
A
- Abandon vs. abandonment
- Abdicate, abnegate, abrogate
- Abided vs. abode
- Ability vs. capability vs. capacity
- Abject vs object
- Abjure vs. adjure
- Abolishment vs. abolition
- Aborted vs. abortive
- Abracadabra – Usage, Origin & Meaning
- Absolve vs resolve
- Abstruse vs. obtuse
- Accell
- Access
- Access vs excess
- Accidental vs occidental
- Acclimate, acclimatise, acclimatize
- Acclimation vs acclamation
- Accord vs. accordance
- Achilles’ heel
- Acme vs acne
- Acronym vs anacronym
- Adaptable or adaptive
- Adaption vs. Adaptation – What’s the Difference?
- Adapt vs adopt
- Addicting vs. addictive
- Addition vs. edition
- Addlepated, addlebrained and addleheaded
- Adduce vs educe
- Adjudicate
- Administrate
- Admittance vs. Admission – Difference & Definition
- Adolescence vs adolescents
- Adopted vs. adoptive
- Advance vs. advanced
- Advent
- Adverse vs. Averse – Difference, Meaning & Examples
- Advert vs. avert
- Advice vs. Advise – Meaning, Spelling & Examples
- Ad hoc
- Ad Hominem Fallacy Examples and Definition
- Ad Nauseam – Usage, Meaning & Examples
- Ad-lib and ad lib
- Aegis
- Aerie vs airy
- Aerobic vs anaerobic
- Aeroplane vs. airplane
- Aesthetic vs. ascetic
- Aetiology or etiology
- Affective vs. effective
- Affinity vs infinity
- Afflict vs. inflict
- African-American vs. black
- Afterward vs. afterwards
- Afterward vs. afterword
- Aggravate vs aggregate
- Aggravate vs mitigate
- Aggravate – Usage, Meaning & Examples
- Aggression vs. aggressiveness
- Agnostic vs. Atheist – What’s the Difference?
- Agree
- Ahold
- Ailment vs aliment
- Ain’t
- Alas or But Alas – Usage, Punctuation & Meaning
- Albeit
- Alcoholism vs dipsomania
- Algorithm vs logarithm
- Allegation vs accusation
- Alleviate vs elevate
- Alligator vs. crocodile
- Alliterate, literate or illiterate
- Alliteration vs assonance
- Allude vs. elude
- Allusion vs. elusion vs. illusion
- Allusive, elusive or illusive
- All but
- All but vs anything but vs everything but
- All of the Sudden vs All of a Sudden – Which is Correct?
- All right vs. alright
- All that
- All-around, all-round
- Alphabetic vs. alphabetical
- Alternately vs alternatively
- Alternate vs. alternative
- Alter ego
- Although vs. though
- Alumna, Alumnae, Alumni, Alumnus – What’s the Difference?
- Always vs all ways
- Amalgam vs. amalgamation
- Amative or amatory
- Amazeballs
- Amber vs ember
- Ambiguous vs ambivalent
- Ameliorate vs alleviate
- Amend vs. emend
- American
- American Indian vs Native American
- Amiable vs. amicable
- Among vs. Amongst – Difference, Usage & Examples
- Among vs. Between – When to Use Each
- Amoral vs. Immoral – What’s the Difference?
- Amount vs. number
- Amuse vs. bemuse
- Analogue vs. analogy
- Anamorphic
- Anathema
- Ancillary vs auxiliary
- And yet
- Anecdote vs antidote
- Angel vs. Angle – How to Remember the Difference
- Animal Adjectives – Complete List
- Animal collective nouns
- Animate vs adamant
- Annal vs annual
- Annual, perennial or biennial
- Anomalous vs anonymous
- Another think coming
- Antennae vs. antennas
- Antichrist
- Anyplace or Any Place – Which is Correct?
- Anyway vs. anyways
- An historic
- Apartment vs. Flat – What’s the Difference?
- Apiary vs aviary
- Apologetics
- Apoplectic vs apocalyptic
- Apostle
- Apotheosis
- Apposite vs opposite
- Appraise vs. apprise
- Apprehend vs apprehensive
- Apprehend vs comprehend
- Apprehensive vs reprehensive
- Approbation vs opprobrium
- Appropriate vs. expropriate
- April Fool’s or April Fools’
- Apropos
- Argot vs ergot
- Argumentative vs. Argumentive – What’s the Difference?
- Arise or rise
- Around the clock, round the clock
- Around vs. round
- Arouse vs. rouse
- Arrant vs. errant
- Arse vs. Ass – What’s the Difference?
- Artesian vs artisan
- Ascared – Meaning and Usage
- Ascent, ascendance, ascendancy, etc.
- Ascribe vs attribute
- Ascribe vs subscribe
- Askew vs eschew
- Aspiration vs inspiration
- Aspire vs inspire
- Assail vs. assault
- Assure, ensure, insure
- Astrology vs astronomy
- Asylum
- As crook as Rookwood
- As Far As – Meaning & Examples
- As per
- As Thick As Thieves – Meaning & Origin
- As yet, as of yet
- Atlas
- Attain vs. obtain
- At a loose end
- At loggerheads
- At the End of the Day – Usage & Meaning
- Aught or Aughts – Usage & Meaning
- August
- Auspicious vs suspicious
- Authoritative vs. authoritive
- Autobiography vs biography
- Autocorrect
- Autotune or Auto-Tune
- Autumn vs. fall
- Au contraire
- Au pair
- Avail
- Avant-Garde – Meaning and Examples in a Sentence
- Avenge vs. Revenge vs. Vengeance – Difference, Meaning & Examples
- Avocation vs. vocation
- Awaiting vs. Waiting – What’s the Difference?
- Award vs reward
- Away vs a way
- Awfully
- Awry vs wry
- Aw or awe
- Axiom, adage or epigram
- A Friend In Need Is A Friend Indeed – Origin and Meaning
- A hold vs ahold
- A la (à la)
- A leg up
- A Little vs. A Few – Difference, Examples & Worksheet
- A lot vs allot
- A miss is as good as a mile
- A priori
- A Stone’s Throw—A Simple Phrase for Short Distance
- A Whole Nother – Usage and Meaning
- A.M. or P.M. – How to Write Them (+ Examples)
B
- Backward vs backwards
- Backwater or backwaters
- Back in the day
- Back up vs. backup
- Bad penny
- Bad rap vs. bad wrap
- Bae vs bay
- Balmy vs. barmy
- Baloney vs. bologna
- Bamboozle
- Band (together) vs. bandy (about)
- Ban vs. bar
- Barnstorm
- Bar mitzvah and bat mitzvah
- Basis (on a daily basis, on a regular basis, etc.)
- Bastion
- Bathos vs pathos
- Baton vs batten
- Batten Down the Hatches – Meaning and Origin
- Bawdy vs body
- Bawl out
- Bazaar vs. bizarre
- Bear market, bull market, bearish, bullish
- Beat Around the Bush – Origin & Meaning
- Beggar Belief – Meaning and Origin
- Begrudge
- Behalf
- Behest vs bequest
- Belay vs belie
- Belie
- Bellwether
- Bellyache
- Benchmark
- Bereaved vs. bereft
- Beside or besides
- Bête noire
- Betwixt – Usage & Meaning
- Beyond the pale
- Bezel vs embezzle
- Biannual vs. biennial
- Biannual, biennial and semiannual
- Biceps and triceps
- Bid, bade, bidden
- Big-ups
- Bimonthly and semimonthly
- Binded vs. bound
- Binge-Watch or Binge-Watching – Meaning & Examples
- Bingo
- Bisect vs dissect
- Bit vs. bitten
- Biweekly vs semiweekly
- Blackmail vs extortion
- Black market
- Black out vs blackout
- Blandish vs brandish
- Blatant vs. flagrant
- Blather vs blabber
- Blather vs. blither
- Blench vs blanch
- Bling
- Blond or Blonde – Difference, Meaning & Spelling
- Bloviate
- Blowhard and windbag
- Blue blood
- Bobbsey twins
- Bodega
- Boggle the mind and mind-boggling
- Bohemian
- Bold-Faced Lie or Bald-Faced Lie – Meaning & Origin
- Bona fide, bona fides
- Bone of contention
- Bone to pick
- Bone vs debone
- Bonhomie
- Boondoggle
- Boot camp
- Botanic vs. botanical
- Boughten
- Bound vs. bounded
- Bounteous vs bountiful
- Bourgeois, bourgeoisie
- Brackets vs. Parentheses
- Brainchild
- Brandish vs brand
- Brand spanking new
- Breach, breech, broach
- Breath vs. breadth (vs. width)
- Bric-a-brac and knick-knack
- Bridle vs. bridal
- Bring vs take
- Briton
- Broach vs. brooch
- Brung, brang
- Buck Naked vs. Butt Naked – Which Is Correct?
- Buffer vs. buffet
- Build up vs. buildup
- Bullion vs boullion
- Bullseye or bull’s eye
- Bully pulpit
- Bumpkin
- Bum-rush vs bum’s rush
- Bunk, bunkum, buncombe
- Bunny vs Bunnie
- Burgle vs. burglarize
- Burned vs. Burnt – Difference, Definition & Examples
- Burnish vs tarnish
- Burnout vs. burn out
- Bursted
- Burthen
- Busybody
- Butterfingers
- Butter wouldn’t melt in his mouth
- Butt (Bump) Heads—The Challenge of Conflict
- But vs. yet
- Buzzword
- By and by vs. by the by
- By dint of
- B Line or Beeline – Origin & Meaning
C
- Cacao vs. cocoa
- Cache vs. cachet
- Cacti vs. Cactuses – Which Is the Correct Plural Usage?
- Caddy-Corner, Kitty-Corner or Catty-Corner
- Caduceus vs staff of Asclepius
- Calfs or Calves – Usage, Difference & Examples
- Callous vs. callus
- Calvary vs. cavalry
- Canard
- Canary in the coalmine
- Candy corn
- Cannot or Can Not – Usage, Difference & Examples
- Canny vs uncanny
- Cantankerous
- Canvas vs. canvass
- Can goods or canned goods
- Can of worms vs pandora’s box
- Can vs may
- Can’t vs cant
- Capital vs. Capitol – Usage, Difference & Examples
- Capitulate vs recapitulate
- Capstone, keystone or cornerstone
- Captivate vs capture
- Caramel vs carmel
- Carbon copy
- Card Shark or Card Sharp – Origin & Meaning
- Careen vs. career
- Caretaker vs caregiver
- Carnation vs incarnation
- Carnivore, herbivore or omnivore
- Carrot, carat, karat, caret
- Carte blanche
- Car park vs parking lot
- Casket vs coffin
- Cassandra
- Casted – Usage and Meaning
- Caste vs cast
- Cast Aspersions or Dispersions – Difference & Meaning
- Cast the First Stone—An Important Lesson in Judgement
- Cast-Iron Stomach—How to Eat Anything and Not Feel Sick
- Catch-22
- Cattle vs chattel
- Cauterize vs cauterise
- Cavalcade
- Caveat
- Cease and desist
- Cede vs. concede
- Celebrant or celebrator
- Celiac or coeliac
- Center around or center on
- Century or Centuries – Usage and Meaning
- Ceremonial vs ceremonious
- Certainty vs. certitude
- Chafe vs. chaff
- Chain letter
- Chaise lounge and chaise longue
- Chalk up vs. chock
- Champing at the Bit vs. Chomping at the Bit – Meaning and Origin
- Character or caricature
- Charade and charades
- Charism vs charisma
- Charlatan
- Chasten vs. chastise
- Chaste vs chased
- Cheek by jowl
- Cheek to cheek vs cheek-to-cheek
- Childlike vs. Childish – What’s the Difference?
- Chills down the spine
- Chink vs. kink
- Chinwag
- Chips vs. fries
- Choate or inchoate
- Chortle
- Chose vs. Choose – Usage With Examples
- Cisgender vs transgender
- Cistern vs sister
- Civil rights and human rights
- Clamor vs clamber
- Classic vs. classical
- Cleanup vs. clean up
- Clean vs. cleanse
- Cleave
- Clench vs. clinch
- Client vs. Customer – Difference in Meaning & Usage
- Cliffhanger
- Cliffs Notes
- Climactic vs. climatic
- Closer vs closure
- Cloture vs closure
- Cloying and mawkish
- Cockamamie
- Coddle and mollycoddle
- Cognate and false cognate
- Coiffure vs coiffeur
- Cold-call
- Collaborate vs corroborate
- Collectible vs collectable
- College vs. University – Usage, Difference, & Meaning
- Collegial vs. collegiate
- Collision vs collusion
- Coma vs comma
- Comb-over
- Comedienne
- Come over vs overcome
- Come-hither look
- Comic vs. comical
- Coming Down the Pike vs. Coming Down the Pipe
- Comity vs comedy
- Commencement
- Commend vs command
- Commentator vs. commenter
- Commiserate vs commensurate
- Compared To or With – Which One To Use?
- Compel vs. impel
- Complacent vs complicit
- Complacent vs. complaisant
- Complement vs. compliment
- Compose vs. comprise
- Comprise vs compromise
- Compunction vs compulsion
- Concave vs. convex
- Conceive vs. perceive
- Concerning – Usage, Meaning & Synonyms
- Concerted
- Conches vs. conchs
- Concurrent vs consecutive
- Condemn vs. condone
- Confidant vs. confidante
- Confirmation bias
- Conflate vs conflagrate
- Conflict of interest
- Congruent vs. congruous
- Connect the Dots—A Simple Idiom for Analysis
- Connive vs contrive
- Connote vs. denote
- Conscience, conscious and self-conscious
- Conservatory, solarium or sunroom
- Consolation vs constellation
- Conspiracy or collusion
- Contaminate vs contaminant
- Contemporaneous vs. contemporary
- Contemptible vs. contemptuous
- Content or Contented vs. Contently or Contentedly
- Contiguous vs continuous
- Continental breakfast
- Contingency vs contingent
- Continual vs. Continuous – Usage, Difference & Examples
- Contravene vs contradict
- Contronym and auto-antonym
- Conversate
- Convivial vs congenial
- Convocation, commencement or invocation
- Coon’s Age – Meaning, Origin and Examples
- Coop, coup or coupe
- Cooties
- Copyright vs. copywrite
- Core, corps and corpse
- Cornet vs. coronet
- Corollary vs. correlation
- Corroborate vs cooperate
- Cosmetology vs. cosmology
- Cosset vs corset
- Cottage industry
- Could have, could’ve or could of
- Counsel vs consul
- Coups vs. Coos
- Coup de grace
- Covert vs overt
- Cover all the bases
- Covet vs covert
- Co-op vs. co-opt
- Crackerjack
- Crapshoot
- Crave vs craven
- Crayfish, crawfish, crawdad, etc.
- Crayon vs Crayola
- Cream of the crop
- Creature comfort
- Crèche and manger
- Credible vs. credulous
- Credible, creditable or credulous
- Creeped or Crept – What’s the Difference?
- Crevasse vs. crevice
- Crews vs. Cruise
- Crick (variant of creek)
- Criteria, criterion
- Cross vs crucifix
- Crowdsourcing vs crowdfunding
- Cruciferous
- Cryptid
- Cry Wolf – Idiom, Meaning and Sentence Examples
- Culpable vs liable
- Cul-de-Sac – Usage, Meaning & Spelling
- Cum
- Curmudgeon
- Currently – Correct Usage, Grammar and Examples
- Cursory vs curse
- Custom vs costume
- Cute as a Button – Origin and Meaning
- Cut and dried
- Cut off your nose to spite your face
- Cut the Mustard – Meaning and Origin
- Cut to the Chase – Meaning & Origin
- Cut-throat
- Cyclist vs. biker
- Cynical
- C’est la vie
D
- Dampen, damper, dampener
- Dance on someone’s grave
- Daresay
- Dark horse
- Data Is or Data Are? – The Singular vs. Plural Debate
- Davy Jones’s locker
- Daylight Saving Time or British Summer Time
- Days vs. Daze
- Deaf vs deft
- Dealed or Dealt – What’s the Past Tense of Deal?
- Dearth
- Debark or disembark
- Debauchery
- Decathlon, heptathlon, pentathlon, triathlon and biathlon
- Deceptively
- Decidedly
- Decimate
- Decisive vs divisive
- Deconstruction
- Decrepit vs deprecate
- Decry vs. descry
- Deduce vs. induce
- Deduct vs deduce
- Deep-seeded vs. deep-seated
- Defenestration
- Definite vs definitive
- Defuse vs. diffuse
- Deign
- Déjà vu
- Delegate vs relegate
- Delude vs dilute
- Delusions of grandeur
- Demon vs daemon
- Demur vs. demure
- Denounce vs. renounce
- Dent vs dint
- Depose vs dispose
- Deposition vs disposition
- Depository vs. repository
- Depravation vs deprivation
- Deprecate vs. depreciate
- Depute vs dispute
- Derision vs decision
- Descendant vs. descendent
- Desert vs. Dessert – When to Use Each One
- Desolate vs destitute
- Desperate vs disparate
- Despite vs. In Spite Of – Difference & Meaning
- Destroy vs. destruct
- Deteriorate vs decline
- Detract vs. distract
- Device vs. devise
- De facto
- De rigueur
- Dharma and karma
- Dialectal vs. dialectical
- Diamond in the rough
- Diaspora
- Dice vs. Die – Which Is Singular and Which Is Plural?
- Dichotomy vs discrepancy
- Dichotomy vs paradox
- Dickensian
- Didactic vs pedantic
- Dieresis and diaeresis
- Difference Between Tell and Say – Examples & Worksheet
- Difference vs deference
- Different from, different than, different to
- Diktat
- Dilapidated
- Directional words
- Dirigible or blimp
- Disabuse, misuse and abuse
- Disassemble vs. dissemble
- Disburse vs. disperse
- Discomfit vs. discomfort
- Disconnect
- Discrete vs. discreet
- Disenfranchise vs. disfranchise
- Disillusion vs. dissolution
- Disinterested vs. uninterested
- Disparity vs disparateness
- Dispense with vs. dispose of
- Disposed vs. predisposed
- Dissociate vs. disassociate
- Distaff
- Distinct vs. distinctive
- Distrust vs. mistrust
- Divers vs. diverse
- Divorcée, divorcé, divorcee
- Docent
- Dogged vs dogged
- Doggerel
- Dog days
- Dominant vs predominant
- Don’t look a gift horse in the mouth
- Don’t’s or don’ts
- Doodle
- Doomsday vs Domesday
- Doppelgänger
- Dossier
- Dos or do’s
- Dotage vs senility
- Dotard
- Double entendre
- Double jeopardy
- Double vs. redouble
- Double-edged sword
- Doubtlessly
- Dove vs. dived
- Downfall vs. downside
- Downplay or play down
- Downright vs outright
- Doyen or doyenne vs docent
- Do and Make Exercises (with Printable PDF)
- Do apologize
- Do, Does, Am, Is & Are Exercises (With Printable PDF)
- Dragged vs. drug
- Draw a line in the sand
- Dreamed or Dreamt – What’s the Past Tense of Dream?
- Dredge vs drudge
- Dregs vs dredge
- Dribble vs. drivel
- Dribs and drabs
- Drier vs. dryer
- Drink the Kool-Aid
- Drink, Drank or Drunk – What is the Past Tense Of Drink?
- Drive-by
- Droid vs. Android vs. Robot – What’s the Difference?
- Droll
- Drop off vs. drop-off (vs. dropoff)
- Drop-dead vs drop dead!
- Dry goods
- Dudgeon vs dungeon
- Due to vs because of
- Duly Noted – Meaning, Usage & Examples
- Duly vs dully
- Dumb down
- Dumb waiter and dumbwaiter
- Duplicate vs duplicity
- Duplicate vs replicate
- During the course of
- Du jour
- Dwarfs vs. dwarves
- Dwelled vs. dwelt
- Dyed in the wool
- Dystopia or utopia
- D’oh
E
- Each other vs. one another
- Earnest vs Ernest
- Earthy vs. earthly
- Earworm
- Easter egg
- Easy pickings
- Ecclesiastical and ecclesiastic
- Eclipses vs ellipsis
- Economics vs. finance
- Economic vs Economical – Definition & Examples
- Effable vs affable
- Eggnog
- Egregious vs gregarious
- Either vs ether
- Elbow grease
- Elder, Eldest or Oldest – What’s the Difference?
- Electric, electrical, electronic
- Elegy vs. eulogy
- Elfs vs. elves
- Elocution vs. locution
- Embolization and embolisation
- Emeritus – Meaning & Definition
- Emigrate vs Immigrate – What’s the Difference?
- Eminent vs. immanent vs. imminent
- Emission vs omission
- Emolument vs emollient
- Empathetic vs. empathic
- Empathy vs. sympathy
- Empire vs umpire
- Endear or Endeared – Usage and Definition
- Endeavor vs. endeavour
- Endorphin
- Enervate vs energize
- Enervate vs. innervate
- England, Great Britain, United Kingdom
- Enjoin vs join
- Enormity vs. enormousness
- Ensconce vs sconce
- Enthuse
- Entitled vs. titled
- Entomology vs. etymology
- Entree vs entrée
- Envision vs. envisage
- En Dash vs. Em Dash vs. Hyphen – How to Properly Use Them
- En route
- En vogue, in vogue
- Épée, foil or sabre
- Epicenter
- Epic vs epoch
- Epidemic vs. Pandemic
- Epigram vs. epigraph
- Epiphany or Twelfth Night
- Epitaph vs epithet
- Epithet vs sobriquet
- Epitome vs epiphany
- Eponymous
- Equable, equatable, equitable
- Equator vs prime meridian
- Equivalence vs. equivalency
- Equivocate vs prevaricate
- Ergo
- Ergonomics
- Erratum, addendum and corrigendum
- Ersatz
- Erupt vs irrupt
- Especially vs specially
- Espouse vs expound
- Espresso vs. expresso
- Estimate vs. estimation
- Ethereal vs ephemeral
- Ethics vs. Morals – Definition, Difference & Examples
- Ethnicity vs. race
- Ethnic vs ethic
- Et Al. – Meaning, Punctuation and Usage With Examples
- Et cetera (etc.)
- Evacuate
- Evade vs invade
- Even Keeled or Even Keel – Usage & Meaning
- Everyday vs. Every Day – What’s the Difference?
- Everyone vs every one
- Ever and Never – Usage, List of Examples & Worksheet
- Exacerbate vs exasperate
- Exalt vs. exult
- Exceed vs accede
- Excited vs exited
- Excoriate vs execrate
- Excrete vs secrete
- Exculpate vs exonerate
- Exemplary – Meaning and Examples in a Sentence
- Exercise vs. exorcise
- Exhibit vs. exhibition
- Exhort vs extort
- Existential – Meaning & Definition
- Existent vs. extant
- Expatriate vs immigrant
- Expectant vs. expecting
- Expedient vs expeditious
- Expedite vs expedient
- Expiration date and expiry date
- Explicate vs expletive
- Explicit vs implicit
- Expose vs exposé
- Expound vs expand
- Extant vs extent
- Extemporaneous
- Extradite vs expedite
- Extraordinaire
- Extricate vs extirpate
- Exuberant vs exorbitant
- Ex post facto
F
- Factious vs fractious
- Factoid
- Fail vs flunk
- Fain vs. feign
- Fairy-tale ending
- Fair vs. fare
- Fait accompli
- Faker vs fakir
- Fallow vs follow
- Falseness vs. Falsity vs. Falsehood – Meaning & Definition
- Fame vs defame
- Famous, infamous and notorious
- Faraway vs far away
- Farther vs. Further – Difference, Definition & Examples
- Far East, Middle East, Near East
- Fastly
- Fatal vs fateful
- Fatuous vs facetious
- Faux
- Faux pas
- Fay, fey
- Faze vs. phase
- Fearful vs. fearsome
- Feckless vs reckless
- Feminity vs. femininity
- Ferret out
- Fervent vs. fervid
- Festivus
- Fete
- Fewer vs. Less
- Fiancé vs. fiancée
- Fictional vs. fictitious
- Fiction vs. nonfiction
- Fiefdom
- Fifth column
- Figurehead
- Filet vs. fillet
- Filibuster
- Financer vs. financier
- Finger-licking good
- Firefight
- Fireplace vs hearth
- Firing line vs. line of fire
- Firsthand and secondhand vs first-hand and second-hand
- Firstly, Secondly, Thirdly, Etc.
- First aid
- First Floor – Meaning & Spelling
- First World problem
- First-world, third-world
- Fish or Fishes – What is the Plural of Fish?
- Fit vs. fitted
- Flagellants vs flatulence
- Flair vs. flare
- Flammable vs. inflammable
- Flash in the pan
- Flat out
- Flaunt vs. flout
- Flautist vs. flutist
- Fleshly vs. fleshy
- Flesh out vs. flush out
- Flied – Meaning & Definition
- Flip one’s lid vs. flip one’s wig
- Flora and fauna
- Flotsam and jetsam
- Flounder vs. founder
- Flummox
- Fluorescent vs incandescent
- Fly-by-night
- Folderol
- Foley
- Follow up vs. Follow-up vs. Followup – Which is Correct?
- Font vs fount
- Food Coma – Meaning & Examples in a Sentence
- Foolproof vs. full-proof
- Fool’s errand
- Foot long
- Fora vs. forums
- Forbear vs. forebear
- Forbidding vs. foreboding
- Forceful vs forcible
- Force majeure
- Forego vs. forgo
- Formally vs formerly
- Former vs. Latter – Usage With Examples
- Formulas vs formulae
- Fortnight
- Fortuitous vs. fortunate
- For heaven’s sake
- For the purpose of
- For, four and fore
- Fosbury flop
- Fox guarding the hen house
- Fractious vs fracas
- Frankenstein’s monster
- Frankincense and myrrh
- Fraud or defraud
- Fraught
- Frenemy
- Freudian slip
- Fritter away
- Frivolity vs. frivolousness
- Full stop vs. period
- Full-Fledged or Fully Fledged – Meaning & Difference
- Fulsome
- Funereal
- Fungi vs. funguses
- Funner, funnest
- Furlough
- Furor vs. furore
- Fur vs fir
- Fusillade vs fuselage
- Fusion vs confusion
- Futz vs. Putz or Futzing Around vs. Putzing Around
G
- Gaff vs. gaffe
- Gallimaufry
- Gallop vs Gallup
- Gambit
- Gamut vs gambit
- Gantlet vs. gauntlet
- Garbage In, Garbage Out—Impact on Productivity
- Gargle vs. gurgle
- Gargoyle or grotesque
- Garner vs garnish
- Garnish vs garnishee
- Gaslighting – Usage, Meaning & Examples in a Sentence
- Gasses vs. Gases – Which Is the Correct Plural?
- Gavel-to-Gavel – Meaning & Examples
- Gender vs engender
- Gender vs. sex
- Gentle vs genteel
- Gentrification
- Geographic vs geographical
- German vs germane
- Gerrymander
- Gesture vs jester
- Getaway vs get away
- Getting Hitched – Origin and Meaning
- Get religion
- Get, Got or Gotten – When & How to Use Correctly
- Ghost vs ghoul
- Gibberish
- Gibe, jibe, jive
- Gift (as a verb)
- Gilding the Lily—An Idiom from Florals to Fables
- Gimlet eye and gimlet cocktail
- Gleam vs glean
- Glib
- Glom onto
- Gobsmacked
- Goes without saying
- Goldbrick
- Golden ticket
- Gonna
- Goodly
- Good vs well
- Goose-step
- Gourmet vs gourmand
- Governance vs. government
- Go down a treat
- Go for the Jugular—Zero In on One’s Weakness
- Graffiti
- Grammar vs. usage
- Grandfather (as a verb)
- Grateful vs. gratified
- Gratis, gratuitous and gratuity
- Great Scott!
- Gregarious vs garrulous
- Grenadine vs grenade
- Grieve vs aggrieve
- Grill vs. grille
- Grinch – Usage, Meaning & Examples
- Grinded
- Grok
- Gross vs net
- Ground zero
- Gruel vs grueling
- Guarantee vs guaranty
- Gumption
- Guyline vs guideline
- Gymnasia vs. gymnasiums
H
- Habeas corpus
- Habit vs habitat
- Hail vs. hale
- Hairy vs. harry
- Half-mast vs. half-staff
- Halitosis
- Halve or Half – Difference, Usage and Meaning
- Handful, handfuls
- Handicap vs. handicapped
- Hands down
- Hand-me-down
- Hand-wash
- Hangar vs. hanger
- Hangdog
- Hanged vs. Hung – Usage, Difference & Examples
- Hanker vs hunker
- Hanky-panky
- Happenstance – Usage & Meaning
- Harbinger
- Hardy vs. hearty
- Hard (Bitter) Pill to Swallow—The Unpleasant Truth
- Harridan and harpy
- Hash out, thrash out
- Haste Makes Waste – Origin & Meaning
- Hatemonger and hate-mongering
- Haughty vs hottie
- Hawk vs. hock
- Haymaker
- Heads-Up – Usage, Meaning & Definition
- Healthful vs. healthy
- Hear vs listen
- Heavens to Murgatroyd – Idiom, Definition and Origin
- Hector
- Heebie-jeebies
- Helpless vs hapless
- Helter skelter or helter-skelter
- Hence – Usage, Definition & Examples
- Henpeck
- Herbivorous vs herbaceous
- Heretofore or hitherto
- Heroin vs. heroine
- Heterogeneous vs. heterogenous
- Hew vs. hue
- Heyday
- Hieroglyph vs hierograph
- High five
- High on the hog
- Hijinks or high jinks
- Hippocratic vs hypocritical
- Hippogriff or griffin
- Hippopotami, hippopotamuses, hippos
- Historic vs. Historical – Usage and Examples
- Hoax
- Hocus-pocus
- Hokey-pokey, hokey-cokey and hokey-tokey
- Hold My Beer – Origin, Meaning and Usage
- Hold someone’s feet to the fire
- Hold sway
- Holier-than-thou
- Holly vs holy
- Homely vs. homey
- Homily vs. Sermon – Difference, Meaning & Examples
- Homogenous vs. homogeneous
- Homonyms – Definition, Examples and Worksheet
- Homophones, Homonyms, Homographs – Differences and Examples
- Homo sapiens
- Honcho
- Hoodwink
- Hoopla
- Hoover vs. vacuum
- Hooves or hoofs
- Hoping vs hopping
- Horn of plenty and cornucopia
- Horticulturist vs arborist
- Hot spot or hotspot
- How to Use Attend to vs. Tend to Correctly
- How to Use Cannot See the Forest for the Trees Correctly
- How To Use Cue vs. Queue Correctly
- How to Use Forecast vs. Forecasted Correctly
- How to Use Get Down to Brass Tacks (Tax?) Correctly
- How to Use Learnings Correctly
- How to Use Perchance Correctly
- How to Use So and Such – Examples & Worksheet
- How to Use Stank vs. Stunk Correctly
- How To Use Transgender vs. Transsexual vs. Transvestite Correctly
- How to Use ‘Would’ – Guide & Examples
- How’s it going
- Hubris
- Human vs humane
- Humblebrag
- Hunter-gatherer
- Hunt-and-peck
- Hurrah, hooray, hurray
- Hush puppy, hushpuppy or hush-puppy
- Hustle and side hustle
- Hybrid vs highbred
- Hygge
- Hyperbole
- Hyper- vs hypo-
I
- Iconoclast vs heretic
- Ideation vs idea
- Ides of March
- Idiom vs colloquialism
- Idiot savant or savant syndrome
- If you will
- Illegible vs. unreadable
- Imaginary or imaginative
- Imbibe vs imbue
- Imitate vs emulate
- Imitate vs intimate
- Imitate vs intimidate
- Immaculate Conception vs. virgin birth
- Immolate vs emulate
- Immunity vs. impunity
- Impair vs impede
- Impassable vs. impassible
- Impassive vs. passive
- Impending vs. pending
- Imperial vs empirical
- Impetus vs emphasis
- Impinge vs. infringe
- Implosion vs explosion
- Imply vs. infer
- Impractical vs impracticable
- Imprecation vs implication
- Impromptu or improvised
- Impudent vs imprudent
- Impugn vs. impute
- Inalienable vs. unalienable
- Incarnation vs incarceration
- Incase or encase
- Incent vs. Incentivize vs. Incentivise – Meaning & Difference
- Incipient or inchoate
- Incipient vs. insipient (vs. insipid)
- Include, exclude or occlude
- Incommunicado
- Incomparable vs. uncomparable
- Incredible vs. incredulous
- Incubus, succubus
- Indeterminate vs indeterminable
- Indexes or Indices – The Plural Debate
- Indian corn
- Indian Summer – Origin & Definition
- Indiscriminate vs undiscriminating
- Indubitably vs undoubtedly
- Inequality vs. inequity
- Inequity vs. iniquity
- Inexplicable vs. unexplainable
- Infectious vs contagious
- Infect vs. infest
- Inference vs interference
- Inflict vs inflect
- Infomercial
- Infraction vs infarction
- Infuse vs suffuse
- Ingenious vs. ingenuous
- Ingrate vs ingratiate
- Inhabit vs habituate
- Inherent vs inherit
- Innate vs. Enate
- Innocuous vs inoculate
- Inpatient or outpatient
- Inroad vs inroads
- Inside baseball
- Insidious vs invidious
- Insolent vs insolvent
- Instantly vs. instantaneously
- Instigate vs incite
- Instigate vs investigate
- Instill vs install
- Instinctive vs. instinctual
- Intellectual property
- Interment vs. internment
- Internal vs eternal
- Intern vs inter
- Interpretative vs. interpretive
- Inter-, intra-
- Inure vs enure
- Invaluable vs. Valuable – What’s the Difference?
- Invention vs intervention
- Inventive vs innovative
- Inviolable vs inviolate
- Invite (as a noun)
- Invoke vs. Evoke – What’s the Difference?
- In a manner of speaking
- In due course or in due time
- In Excess Of – Usage & Meaning
- In kind
- In point of fact or in fact or as a matter of fact
- In Terms Of – Usage & Meaning
- In the affirmative
- In the course of
- In the Midst of – Usage & Meaning
- In the Offing – Idiom, Origin and Meaning
- In the Process of – Meaning & Definition
- In the throes of
- In This Day in Age or Day and Age – Usage & Meaning
- Ipso Facto – Meaning and Examples
- Irk
- Ironic
- Ironical – Usage, Meaning & Examples in a Sentence
- Is Costed a Word? What is the Past Tense of Cost?
- Is Irregardless a Word? What Does it Mean?
- Is it Ascent or Assent – What’s the Difference?
- Is It God Speed or Godspeed? – Meaning & Usage
- Is It Savy or Savvy? – Definition & Correct Spelling
- Itchy feet
- Iteration
- It And There – Usage, Difference & Worksheet
- It’s not rocket science
- Ivy League
- I Could Care Less – Usage & Meaning
- I Rest My Case—From Courtrooms to Conversations
- I.e vs. E.g – Usage, Meaning & Examples
J
- Jackalope
- Jackanapes
- Jack-in-the-box
- Jack-o’-lantern and Halloween lantern
- Jaded
- Jalousie window vs louvre window
- Jam vs. jamb
- Janus-faced
- Jaywalking
- Jealousy vs envy
- Jersey vs guernsey
- Jet Lag – Meaning & Definition
- Je Ne Sais Quoi (or Jenesequa) – Meaning In English
- Jiggery-pokery
- Jig vs gig
- Jingle vs jangle
- Jingoism
- Jolly Roger
- Joshing – Origin and Meaning
- Joyful and joyous
- Judicial vs. judicious
- Juggernaut
- Junction vs. juncture
- Jury-rig, jerry-rig, jerry-built
- Juvenile vs juvenal
- Juxtapose
K
L
- Lagniappe
- Laird vs lord
- Laissez-faire
- Lambaste
- Lassitude, lethargy and languor
- Latchkey kid and latchkey child
- Later vs latter
- Latitude vs longitude
- Latter vs ladder
- Laughing Stock – Usage, Meaning and Origin
- Laundry list
- Lava vs magma
- Lay vs. Lie – Usage, Difference & List of Examples
- Lazy Susan
- Lede vs. Lead – Usage, Meaning & Examples
- Leery vs leary
- Legislator vs legislature
- Lended vs. lent
- Lend vs. loan
- Lest
- Liable vs libel
- Lie or lye
- Lighted vs. lit
- Like gangbusters
- Limbo
- Limelight vs spotlight
- Lip-sync and lip-synch
- Literally vs. Figuratively – What’s the Difference?
- Liter or litre vs litter
- Litmus test
- Little to No or Little to None – Meaning, Uses and Examples
- Lock out vs lockout
- Logo
- Log On or Log In – What’s the Difference?
- Lonely vs. lonesome
- Longetivity vs. longevity
- Long in the tooth
- Long johns vs union suit and combination suit
- Loose vs. Lose – Difference & Meaning
- Lorem Ipsum
- Lose the plot
- Lothario
- Lots of vs a lot of
- Lo and Behold or Low and Behold
- Lucid vs lucent
- Lumber vs lumbar
- Luminary vs luminaria
- Lustful vs. lusty
- Luxuriant vs. luxurious
M
- Macabre
- Macaron vs. macaroon
- Machine gun vs. machine-gun
- Maddening vs. madding
- Magical realism
- Magnate vs. magnet
- Magnum opus
- Makeup, make-up or make up
- Make do vs. Make Due – What’s the Difference?
- Make hay
- Make or Do – Difference, Examples & Worksheet
- Maleficent vs. malevolent
- Manic vs maniac
- Marginalize or marginalise vs minimize or minimise
- Marinade vs. marinate
- Marsala vs masala
- Massage vs message
- Masterful vs. masterly
- Materiel vs. material
- Matriculate vs graduate
- Matter of fact or matter-of-fact
- Matter of Fact vs. Fact of the Matter
- Maul vs. mull
- Maundy Thursday
- Maverick
- Maxima vs. maximums
- May be or maybe
- Mealy-mouthed
- Means
- Mean vs mien
- Mediator vs. moderator
- Media vs. Mediums – What’s the Difference?
- Melted vs. molten
- Meme
- Memento Mori or Momento Mori – Origin & Meaning in English
- Mendacity vs mendicity
- Meretricious vs meritorious
- Meritorious vs maritorious
- Merry Christmas vs Happy Christmas
- Metaphor
- Methinks
- Mexican standoff
- Mice vs. mouses
- Microfinance, microcredit and microloan
- Micro- vs macro-
- Mic Drop – Origin, Meaning & Sentence Examples
- Might vs mite
- Milieu
- Minima vs. minimums
- Minimum vs minimal
- Minutia, minutiae
- Misfeasance vs. Malfeasance vs. Nonfeasance
- Misinformed vs. uninformed
- Misogyny and misandry
- Mixtape
- Mob justice and mob rule
- Mob or demob
- Modern
- Modus operandi (m.o, MO)
- Mogul
- Mojo
- Molotov cocktail
- Momentarily – Usage & Meaning
- Money-grabbing vs. money-grubbing
- Montage
- Moonlight
- Moonshine
- Moot vs. mute
- Morality vs mortality
- Moral vs morale
- Morays vs. mores
- Morbid vs moribund
- Moreso
- Mortar board
- Motive vs motif
- Mouthfuls
- Movable feast
- Mowed vs. mown
- Mr., Mrs., Ms. and Miss – Full Form and Meaning
- Muchly
- Much or Many – Usage, Difference & Examples
- Muckamuck, mucky-muck and muckety-muck
- Muckraking
- Mumbo Jumbo – Origin and Meaning
- Murderers’ row
- Myriad
N
- Namby-pamby
- Nary a
- Naught vs. nought
- Nauseating vs. nauseous
- Naval vs. navel
- Nebula vs nebulous
- Neck and Neck Meaning and Examples
- Necropsy and autopsy
- Necrosis
- Needle vs nettle
- Nefarious
- Negative prefixes
- Neither or Either – What’s the Difference?
- Nepotism
- Nest egg
- Ne’er-do-well
- NGO vs GMO
- Nickname
- Niggle
- Night owl or early bird
- Nip in the Bud – Origin & Meaning
- Nitty-gritty
- Noblesse oblige
- Noble vs ignoble
- Nocturnal vs diurnal
- Noisome vs noisy
- Nomenclature
- Nonplussed
- Nonprofit vs. not-for-profit (vs. non-profit)
- Non sequitur
- Normalcy vs. normality
- Nosy Parker
- Notwithstanding
- Not hardly
- Not un-
- Noxious vs obnoxious
- No vs. Not – Usage, List of Examples & Worksheet
- No-brainer
- Number vs numeral
- Numinous vs luminous
- Nunchucks
O
- Object lesson
- Obliged vs. obligated
- Oblique
- Obsequious
- Observance vs. observation
- Obsolescent vs. obsolete
- Obstreperous
- Octopuses vs. Octopi – What Is the Plural of Octopus?
- Odious vs odorous
- Oeuvre – Usage and Meaning in English
- Offhand
- Off Of – Usage & Meaning
- Off the cuff
- Off The Wagon and On The Wagon – Meaning & Examples
- Off-kilter and out of kilter
- Oftentimes
- Oh Well – Usage & Meaning
- Old Glory
- Old Hat – Idiom, Origin & Meaning
- Oligarchy vs monarchy
- Olive branch
- Omnibus vs ombudsman
- Onboard vs. On board
- Once Bitten, Twice Shy – Idiom, Meaning & Origin
- Once in a lifetime vs once-in-a-lifetime
- One and the same, one in the same
- One Fell Swoop – Origin and Meaning
- One-hit wonder
- On Accident or By Accident – Usage & Examples
- On Cloud Nine – Origin & Meaning
- On steroids
- On tenterhooks
- On the fritz
- On the lam
- On the up and up
- Oompa Loompa
- Oppress, repress, suppress
- Oracle vs auricle
- Oral vs. verbal
- Ordinance vs. ordnance
- Orientate
- Ouster
- Outset vs onset
- Outside of
- Out and out
- Out of Pocket – Meaning, Origin, & Definition
- Out of the blue vs out of the woodwork
- Overlook vs look over
- Overly
- Overnight vs. over night
- Overrate vs overate
- Oversee vs overlook
- Overtake, take over and takeover
- Overthink vs think over
- Overtones vs. undertones
- O vs. Oh – Usage, Meaning & Examples
P
- Paddy wagon
- Paean, paeon, peon
- Pall vs. pallor
- Palpable vs palatable
- Pander vs ponder
- Panhandle
- Parade float
- Paralympics
- Parameter vs perimeter
- Paramount vs. tantamount
- Pariah vs piranha
- Parlay vs. parley
- Parlor or parlour
- Parody vs parity
- Parricide vs. patricide
- Part and parcel
- Par Excellence – Usage, Meaning & Examples
- Passed vs. past
- Pass muster
- Pastime vs past time
- Past master
- Pathetic vs apathetic
- Patois
- Patriotism vs nationalism
- Patron vs. Benefactor – Difference & Definition
- Paucity – Meaning & Examples in a Sentence
- Payback vs. pay back
- Pay the Piper – Idiom, Meaning & Origin
- Peaceable vs. peaceful
- Peace of mind, piece of (one’s) mind
- Peccadillo
- Pecking Order – Origin and Meaning
- Pedal vs. peddle vs. petal
- Pediment vs impediment
- Pejorative
- Penal vs. penile
- Penchant vs pension
- Pendant vs. Pendent – Meaning & Difference
- Pentimento vs pimento or pimiento
- Penultimate
- Peplum vs pablum
- Peremptory vs pre-emptory
- Perfect Storm – Idiom, Origin & Meaning
- Perfunctory vs peremptory
- Periodic vs. Periodical – Origin, Usage and Examples
- Peripatetic
- Perjury
- Perk vs perq
- Permit vs permit
- Pernickety vs. persnickety
- Perpetrate vs perpetuate
- Perquisite vs. prerequisite (vs. requisite)
- Persecute vs. prosecute
- Personal vs personable
- Personal vs personnel
- Persona non grata
- Personification vs anthropomorphism
- Persons vs. People – Proper Usage & Examples
- Perspective vs. prospective
- Peruse
- Pervert vs subvert
- Per diem
- Per Se or Per Say – Usage, Meaning & Examples
- Petroglyph vs pictograph
- Pettifogger
- Petulant vs impetuous
- Pet vs. petted
- Phial vs. vial (vs. vile)
- Phony vs. phoney
- Phosphene
- Photogenic vs photographic
- Picaresque vs. picturesque
- Piebald, skewbald, pinto or paint
- Pied Piper
- Piggyback
- Piggy bank
- Pincer vs. pincher
- Pink slip
- Piping Hot – Origin & Meaning
- Pissant
- Pitchblende
- Pitcher vs picture
- Pith vs pit
- Placate vs placket
- Place card vs placard
- Plainclothes
- Plaintiff vs defendant
- Plaintive vs plaintiff
- Plain vs. plane
- Plaque vs plack
- Play By Ear – Meaning and Usage
- Pleaded or Pled – Definition & Examples
- Plenary vs preliminary
- Plenitude vs. plentitude
- Plethora
- Plug-ugly vs pug-ugly
- Plutocrat vs autocrat
- Podium vs lectern
- Poetry vs prose
- Pogrom vs genocide
- Point in time
- Point of view, standpoint, viewpoint
- Point-blank
- Poisonous vs venomous
- Polemic vs Polemical – What’s the Difference?
- Politics
- Polka dot
- Polygamy vs. polygyny vs. polyandry
- Ponderous
- Ponzi scheme and Ponzi game
- Poor sport, sore loser and sore winner
- Poo vs. pooh
- Popinjay
- Poppycock
- Pop culture
- Porch vs. Veranda vs. Verandah – Difference & Definition
- Portend vs pretend
- Portend vs. portent
- Port vs. starboard
- Poseur vs poser
- Possibility vs probability
- Poster child
- Potentiality
- Practicable vs. practical
- Practical joke
- Pragmatism
- Praise vs preys
- Pram, baby carriage and baby buggy
- Prank call or crank call
- Precedence vs precedents
- Precipitate vs precipitous
- Precocious vs precious
- Predict vs predicate
- Predominantly vs. Predominately – Usage & Meaning
- Premier vs. premiere
- Preposition vs. proposition
- Prescient vs present
- Prescribe vs. proscribe
- Preserve vs persevere
- Presume vs. Assume – Difference, Meaning & Examples
- Presumptive vs. presumptuous
- Pretentious vs portentous
- Preternatural vs supernatural
- Previous vs. prior
- Primal scream
- Proactive
- Problematic vs. problematical
- Procede vs. Precede vs. Proceed – What’s the Difference?
- Procrastinate
- Prodigal and prodigy
- Progeny vs prodigy
- Proliferate vs profligate
- Promise vs premise
- Prom and The Proms
- Proof is in the pudding
- Prophecy vs. prophesy
- Propitiate vs expiate
- Proportional vs. proportionate
- Proprietary vs propitiatory
- Prostate vs. prostrate
- Protagonist vs. Antagonist – Definitions and Examples
- Protean vs protein
- Protégé
- Proved vs. proven
- Proverbial vs figurative
- Proverb vs adage
- Providence vs province
- Province vs provenance
- Psalter vs salter
- Pseudo
- Psychopath vs. sociopath
- Psych vs. psyche
- Pullout, pull-out, pull out
- Pull strings
- Pull the rug out from under
- Punctilious vs punctual
- Puppy love or poppy love
- Purple prose
- Purposely vs. purposefully
- Purpose vs porpoise
- Pushing Up Daisies – Meaning & Origin
- Putative vs punitive
- Put one’s best foot forward
- Put on heirs or airs
- Put though the wringer vs put through the ringer
Q
R
- Rack vs. wrack
- Radical
- Raise vs rise
- Raison d’etre
- Ramshackle
- Rapt vs. wrapt
- Raring to Go – Meaning and Origin
- Rational or rationale
- Ravaging vs. ravishing
- Raven vs ravenous
- Razzle-dazzle and razzmatazz
- Razzmatazz or razzamatazz
- Reactionary vs. reactive
- Realty vs reality
- Rearranging the deck chairs on the Titanic
- Rebuke vs refute
- Rebus
- Rebut vs refute
- Receipt vs. Recipe – Difference in Meaning & Spelling
- Recur vs. reoccur
- Recuse vs excuse
- Redact vs retract
- Redneck vs. Hillbilly vs. Hick – What’s the Difference?
- Redress vs readdress
- Red herring
- Red tape
- Red-Letter Day – Idiom, Origin & Meaning
- Reed vs read
- Reforested wood
- Refugee vs immigrant
- Regard vs. regards
- Regimen vs regiment
- Regime vs. regimen
- Regrettable vs. regretful
- Regulate vs relegate
- Reindeer or caribou
- Relevancy vs. Relevance – Usage, Difference & Meaning
- Reluctant vs reticent
- Repair vs reparation
- Repel vs. repulse
- Repetitive vs redundant
- Repudiate and refudiate
- Repudiate vs refute
- Repugnant vs pungent
- Reputedly vs reportedly
- Repute vs refute
- Resemble vs reassemble
- Resilience vs. resiliency
- Resolve vs solve
- Respective, respectively
- Restitution vs retribution
- Restrict vs constrict
- Résumé
- Retard
- Retrograde vs anterograde or antegrade
- Retronym
- Retrospect vs introspect
- Reverent vs reverend
- Ridded
- Rife vs. ripe
- Riffraff
- Riffraff vs riprap
- Riff vs. rift
- Righten
- Right-of-way
- Rigor mortis
- Riptide, rip current or undertow
- Risky vs risqué
- Road rage
- Rollout vs. roll out
- Rollover vs. roll over
- Roll Up Your Sleeves – Meaning, Uses, Examples & Origin
- Roman-à-clef
- Roofs vs. rooves
- Rookie
- Root vs. route vs. rout
- Rotate or revolve
- Rotund vs rotunda
- Rot vs. Wrought
- Roux, rue or roué
- Royal “we”
- Rule of thumb
- Rummy
- Runaway vs. run away
- Running on empty and running on fumes
S
- Sabbatical vs sabbath
- Sadist vs. Masochist vs. Sadomasochism – Difference & Definition
- Said
- Said the Actress to the Bishop – Meaning & Origin
- Salacious
- Salubrious vs lugubrious
- Salvage vs selvage or selvedge
- Samovar vs scimitar
- Sanatorium vs sanatarium
- Sanctimonious vs sanctify
- Sanguine vs exsanguinate
- Sang vs sung
- Sank vs. sunk
- Sans – Usage, Meaning & Definition
- Sarcasm
- Sarcophagus vs mausoleum
- Sari vs sorry
- Sartorial vs satirical
- Satire vs satyr
- Satisficing vs satisfying
- Savant vs servant
- Sawed vs. Sod
- Say one’s peace vs piece
- Scared vs scarred
- Scarfs vs. scarves
- Scatological
- Scavenger hunt
- Scavenger, scavenge
- Schadenfreude – Usage & Meaning in English
- Schmooze and shmooze
- Scion
- Scissors
- Scrimp vs skimp
- Scrip vs script
- Scrumdiddlyumptious
- Sculpture vs sculptor
- Seasonable vs seasonal
- Secede vs. succeed
- Second that emotion or notion or motion
- Second-Guess – Usage & Meaning
- Secret Santa
- Secret vs. secretive
- Secular vs sacred
- Security blanket
- Sedimentary vs sedentary
- Sediment vs sentiment
- Sedition vs sedation
- Seldomly – Meaning & Definition
- Self-quarantine vs self-isolation
- Seminal
- Sensual vs. sensuous
- Sentience vs sapience
- Sentient vs sentiment
- Separate vs separate
- Sepulcher, crypt, catacomb or mausoleum
- Sequacious
- Sequins vs sequence
- Series
- Serif vs seraph
- Serigraph vs lithograph
- Service (as a verb)
- Serviette or napkin
- Sever vs severe
- Shaggy-dog story
- Shall vs. will
- Shame vs ashamed
- Shard or sherd
- Share and share alike vs per stirpes
- Shat vs. shitted
- Shaved vs. shaven
- Sheath vs. sheathe
- Shed vs. shedded
- Shelf vs. shelve
- Shell out
- Shenanigans
- Shill vs chill
- Shined or Shone – Difference, Definition and Examples
- Shopping cart or buggy
- Shop till you drop
- Shore vs sure
- Short shrift
- Should have, should’ve or should of
- Shoveled/shoveling vs. shovelled/shovelling
- Showboat
- Sic vs. sick
- Significant Other – Meaning & Origin
- Sign Up vs. Signup
- Silva vs silver
- Silver lining
- Simile
- Sine qua non
- Sisyphean, Promethean or Herculean
- Sitting on a powder keg
- Sit vs set
- Skunkworks
- Slam dunk
- Slap-happy
- Slayed or slew
- Sledge vs sludge
- Sleight of hand
- Slipshod
- Slumgullion and goulash
- Smart alec and smart aleck
- Smite, smote, smitten
- Smooth vs. Smoothe vs. Smoothen
- Smorgasbord
- Snake oil, snake-oil salesman
- Sneaked vs. snuck
- Snipe hunt
- Snitch
- Sob sister and sob story
- Social vs sociable
- Sojourn vs adjourn
- Solder vs soldier
- Soldiers, Marines, Airmen, & Sailors – What’s the Difference?
- Soliloquy vs monologue
- Solitaire and patience games
- Somebody vs. someone
- Someday vs. some day
- Someplace vs. some place
- Something, Anything, Nothing & Everything (With Worksheet)
- Some and Any Exercises (With Printable PDF)
- Some odd
- Some Time vs Sometime vs Sometimes – What’s the Difference?
- Some vs. Any – Usage, List of Examples & Exercises
- Some way vs. someway
- Sooner rather than later
- Sorted vs. Sordid
- Sort Of – Usage, Meaning & Examples
- SOS and Mayday
- Sound bite
- Sow wild oats
- So to speak
- Spanish fly
- Spartan
- Spatter vs. splatter
- Speak to
- Spearhead – Usage & Definition
- Speciality vs. specialty
- Species
- Spectra vs. spectrums
- Sped vs. speeded
- Spiel or Schpiel – Meaning, Spelling & Examples
- Spiffy
- Spilled vs. spilt
- Spinster
- Spite vs respite
- Spit and Image, Spitting Image, or Splitting Image
- Spoiled vs. spoilt
- Spoof
- Spouse vs espouse
- Spreaded
- Spur vs spurn
- Spur vs. spurn
- Squinch
- Stadia vs. stadiums
- Stanch vs. staunch
- Standby vs. stand by
- Stand alone vs standalone
- State of the art
- Stationary vs. stationery
- Statue vs statute
- Status quo
- Statute of limitations
- Stat vs now
- Stir-Crazy – Origin, Usage and Meaning
- Stockholm syndrome
- Stocking stuffer and stocking filler
- Stock vs stalk
- Stock, shares
- Stone cold and stone-cold
- Stool pigeon
- Straight from the horse’s mouth
- Straight vs. strait
- Stratagem vs. strategy
- Striped/striping vs stripped/stripping
- Strived, striven, strove
- Strop vs strap
- Subconscious vs. unconscious
- Subject to vs subjected to
- Subjugated vs subjected to
- Subordinating conjunctions
- Suborn
- Subpoena
- Substantial vs. substantive
- Subtext
- Sub rosa vs sub-rosa
- Sub vs infra
- Suffice to Say or Suffice It to Say – Meaning & Examples
- Suit vs suite
- Sui generis
- Sulk vs skulk
- Summa cum laude or magna cum laude
- Summons and summonses
- Super vs ultra
- Supposably
- Surely vs surly
- Surgeon vs sturgeon
- Surrogacy
- Suspect, person of interest or perpetrator
- Swanning around and swanning about
- Swan song
- Swatch vs swath
- Swath vs. swathe
- Sweat vs. sweated
- Swing for the Fences—Idiomatic Power Play
- Sword of Damocles
- Symbolic vs symbiotic
- Synonyms
- Systematic vs systematical
- Systematic vs. systemic
T
- Tacit vs taciturn
- Tack vs. tact
- Takeaway and takeout
- Taken Back or Taken Aback – Which One to Use?
- Take a toll and take its toll
- Take the mickey out of someone
- Take the reins
- Talk turkey
- Tamper vs temper
- Tanker vs tankard
- Tariff
- Taro vs tarot
- Tartar or tartare
- Tar baby
- Tattletale vs telltale
- Taut vs taunt
- Tease out
- Teetotaler, teetotaller
- Telegram vs. telegraph
- Temblor, tremblor or trembler
- Tenure vs tenor
- Terminate
- Terrific vs terrifying
- Terroir and terror
- Testament vs. testimony
- Tete-a-tete
- Thanksgiving or Thanksgiving Day
- That or Who – When and How to Use Correctly?
- That vs. which
- That which
- Their, them, themselves, they (as singular pronouns)
- Them’s the breaks or brakes
- Then vs. Than – When to Use Each (With Examples)
- Therefore vs therefor
- There Is vs. There Are Exercises (with Printable PDF)
- The Ampersand (&) – How and When to Use It
- The Bronx
- The die is cast
- The end justifies the means
- The jaws of life
- The Late – Usage, Meaning & Examples
- The penny dropped
- The pot calling the kettle black
- The rub
- The vs thee
- The $64,000 question
- Think outside the box
- Third rail
- Thong or flip-flop
- Thoroughbred vs purebred
- Thrall
- Throw the baby out with the bathwater
- Throw under the bus
- Thrust, thrusted
- Thumbs up and thumbs down
- Thusly
- Tic vs. tick
- Tiddlywinks and tiddleywinks
- Till, until, ’til
- Titular
- TMI
- Toe the line
- Toilette
- Toile vs toil
- Toile vs tulle
- Tolerance vs. toleration
- Tomayto, tomahto and potayto, potahto
- Tomfoolery
- Tongue-in-Cheek – Meaning, Origin and Examples
- Tool vs tulle
- Topography vs. typography
- Top banana and second banana
- Torrent vs torrid
- Torturous vs. tortuous
- Touch and go
- Touch base
- Tough row to hoe
- Tour de force
- Tout
- Toxicology vs. toxology
- To a T
- To boot
- To hear crickets
- To the bitter end
- To the nines
- To vs. Too – The Difference With Examples
- To wit
- Track and field and athletics
- Tractable vs trackable
- Tract vs. Track – Difference in Meaning & Usage
- Tragedy vs travesty
- Training wheels vs stabilisers
- Traitor vs trader
- Translucent vs. transparent
- Transparent, translucent and opaque
- Transpire – Definition & Examples
- Transport vs. transportation
- Trap vs entrap
- Trawl vs. troll
- Treatise vs treaties
- Treble vs. triple
- Triage
- Troglodyte
- Trolling
- Troop vs. troupe
- Truck with
- Truculent
- Trustee vs. trusty
- Tsk Tsk or Tisk Tisk – Meaning & Examples
- Tsunami vs tidal wave
- Turbid, turgid, torpid
- Turtle, tortoise, terrapin
- Tussie-mussie vs nosegay
- Twee
- Tween or teen
- Two-bit
U
- Uber
- Ubiquitous
- Udder vs. utter
- Ulterior motive
- Unawares
- Uncle Sam
- Uncomparable adjectives
- Underlie or underline
- Undoubtably vs. undoubtedly
- Unexceptionable vs unexceptional
- Unfamous or infamous
- Union Jack
- Unique
- United States (plural or singular?)
- Unkempt, unkept
- Unknown quantity
- Unsung hero
- Unwitting vs unwilling
- Upfront or Up Front – What’s the Difference?
- Upload vs download
- Upmost vs. utmost
- Upper crust
- Upshot
- Up to date
- Up to snuff
- Urban vs urbane
- Urban, suburban and rural
- Used To or Use To? – Meaning and Examples
- Usually always
- U.S. state demonyms
V
- Vacuous vs. vapid
- Valedictorian and salutatorian
- Vamoose
- Vanguard
- Variance vs variants
- Varied vs various
- Vaudeville
- Vegetarian vs vegan
- Venal vs venial
- Veracity vs. voracity
- Verbatim vs paraphrase
- Verbiage
- Vernacular – Definition & Examples in a Sentence
- Verses vs. versus
- Vertex vs. vortex
- Vertigo vs vertiginous
- Very
- Vested
- Veteran vs veterinarian
- Vice versa
- Vicissitude
- Vigilant vs vigilante
- Vim and vigor
- Viral vs virile
- Vis-a-vis
- Vitiate
- Vittle vs vital
- Viz. – Usage, Meaning and Abbreviation
- Vouchsafe
W
- Waddle vs. wattle
- Wainscot or chair rail
- Waiver vs. waver
- Waive vs. wave
- Wake vs awake
- Wallop and pack a wallop
- Wander vs. wonder
- Wane, wax
- Wangle vs wrangle
- Wanton vs. wonton
- Wary vs. weary
- Washed up or all washed up
- Wassail
- Was vs. Were – Usage, Examples and Worksheet
- Waterloo or meet one’s waterloo
- Water under the bridge
- Watt vs what
- Weakest Link – Usage, Meaning & Examples
- Weaved, wove, woven
- Website vs. web page
- Weekend
- Well-Heeled – Usage, Origin & Meaning
- Wench vs winch
- Were vs we’re
- Wet vs. whet
- Whatnot or What Not – Usage & Meaning
- What Does Leeway Mean? – Usage & Examples
- What Does [Sic] Mean? – Definition & Examples
- What Is Ad Infinitum? – Usage & Meaning
- What Is an Ideologue? – Usage & Meaning
- What Is a Bromance? – Meaning and Examples
- What Is a Byproduct? – Definition and Examples
- What Is a Cavalier? – Usage, Meaning & Definition
- What Is a Charnel House? – Origin & Meaning
- What Is a Conundrum? – Meaning & Examples
- What Is a Dilemma? – Usage and Meaning
- What Is a Glitch? – Usage & Meaning
- What Is a Hat Trick? – Meaning & Origin
- What Is a Hie? – Definition and Meaning
- What Is a Juggalo? – Origin, Meaning & Examples
- What Is a La Carte? – Meaning and Examples
- What Is a Lowlife? – Meaning & Examples
- What Is a Namesake? – Meaning & Examples
- What Is a Pet Peeve? – Meaning, Origin and Examples
- What Is a Prodigal Son? – Meaning, Definition and Origin
- What Is a Raconteur? – Origin, Meaning & Examples
- What Is a Round Robin? – Origin & Meaning
- What Is a Scrooge? – Meaning & Origin
- What Is a Snark? – Usage & Definition
- What Is a White Lie? – Definition, Origin and Examples
- What Is Belated? – Usage, Meaning & Examples
- What Is Chock Full? – Usage, Meaning & Examples
- What is Kith and Kin – Origin & Meaning
- What Is Mea Culpa? – Usage, Meaning & Definition
- What Is Outsource? – Meaning & Examples in a Sentence
- What Is Requiem? – Definition & Meaning
- What Is Trepidation? – Definition & Examples
- Whence vs. from whence
- When to Use Do, Does, Am, Is & Are? (Worksheet Included)
- When to Use “A” or “An”
- Whereas – Usage and Examples in a Sentence
- Whig vs wig
- While away vs. wile away
- Whilst – When & How to Use Correctly
- Whiny, whiney, whinny, Whinney
- Whippersnapper
- Whiskey vs. whisky
- White Christmas
- White Collar vs. Blue Collar – Meaning & Difference
- Whoever vs. whomever
- Whoop vs. whup
- Whose vs. Who’s – Usage, Difference and Examples
- Who vs. Whom – Usage, Rules and Examples (+ Printable Exercise)
- Who’s Who
- Widow, widower
- Wiki
- Will-o’-the-wisp
- Wink vs. Blink – What’s the Difference?
- Win-win or lose-lose
- Wish Exercises (With Printable PDF)
- Wither vs. whither
- Wit vs. whit
- Wobble vs warble
- Wonder vs. wonderment
- Wont
- Wont vs won’t
- Woolgathering
- Word to the wise
- Workout vs. work out
- Work in progress vs work in process
- Worse comes to worst
- Would have, would’ve or would of
- Would just as soon or assume
- Wrap one’s head around
- Wreak Havoc or Wreaking Havoc – Usage, Meaning & Origin
- Wreak vs wreck
- Wrench and spanner
- Writer’s block
- Writ large
- Wrong vs. wrongly
- Wunderkind
