When learning English grammar, one of the more difficult concepts to understand is the present perfect tense. I’ve even struggled with this over the years. But I wrote this article to outline the uses and examples of the present perfect tense and even made a worksheet for you to practice.
So, whether you are a beginner or simply need a refresher, read on as I tell you all you need to know about the present perfect tense!
What Is Present Perfect Tense?
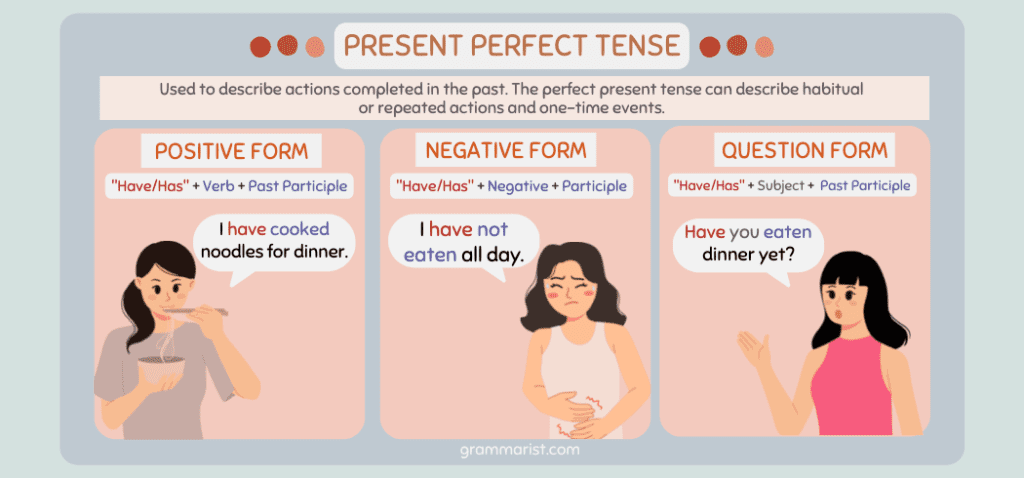
The perfect present tense is a grammatical construction used to describe actions completed in the past. The construction is formed by combining the correct form of the verb “to have” with the past participle of the main verb. The perfect present tense can describe habitual or repeated actions and one-time events.
How Do You Use the Present Perfect Tense?
Good question! The present perfect tense formula uses the present tense of the verb “to have” (I have, you have, he/she has) and the past participle of the main verb (gone, seen, eaten).
For example, “I have gone to the store.”
The present perfect can also be used with adverbs or phrases to signal when the action occurred.
Here are some examples to better show what I mean:
- I have already gone to the store.
- I have just gone to the store.
- I have never gone to the store.
In addition to signaling when an event occurred, the present perfect can be used to describe an event that happened multiple times or is ongoing.
For example:
- I have been to New York three times.
- She has read that book five times.
The present perfect is also used to describe past experiences or states that are still true in the present.
For example:
- I have known her for years.
- They have had a lot of fun
What Are 5 Examples of Present Perfect?
Here are five more examples I created to show the present perfect:
- I have visited that country.
- They have gone to the store.
- We have seen that movie.
- You have moved to a new house.
- She has graduated from college.
What Are the 4 Types of Present Tense with Examples?
There are four main types of present tense in English: the simple present, the present continuous, the present perfect, and the present perfect continuous. Each one has its own use and differs slightly in form from the others.
The Simple Present
The simple present is used to describe habitual or routine actions and give factual information.
For example, “I brush my teeth every morning” or “The sun rises in the east.”
To form a sentence in the simple present, you simply need to use the base form of the verb; there is no need to add -es for third person singular subjects or to conjugate irregular verbs.
The Present Continuous
The present continuous is used to describe actions that are happening right now.
For example, “I am brushing my teeth” or “The sun is rising.”
To form a sentence in the present progressive, you need to use the base form of the verb plus -ing (e.g., “I am writing a paper”). Note that irregular verbs do not follow this pattern and will require you to use a different form.
The Present Perfect
The present perfect describes actions or states that have happened at some point up until now.
For example, “I have brushed my teeth” or “The sun has risen.”
To form a sentence in the present perfect, you need to use the present tense form of have plus the past participle of the verb (e.g., “I have written a paper”). Again, irregular verbs require you to use a different form.
The Present Perfect Continuous
Finally, the present perfect progressive describes actions that started in the past and are still continuing up until now.
For example, “I have been brushing my teeth for two minutes” or “The sun has been rising for an hour.”
To form a sentence in the present perfect progressive, you need to use the present tense form of have plus been plus -ing (e.g., “I have been writing a paper for an hour”).
Present Perfect Tense Rules
The present perfect tense is one of the most difficult tenses for English learners to master. However, it can be used quite easily once you understand the rules. The present perfect tense is formed using the present tense of the verb “have” plus the past participle of the main verb.
For example, the present perfect tense of the verb “read” would be “have read.”
The present perfect tense can describe actions that have recently been completed or are still in progress. It can also be used to describe experiences that happened at an unspecified time in the past.
In addition, the present perfect tense can describe habits or states that began in the past and continue into the present. With a little practice, you’ll be able to use the present perfect tense like a native speaker
When to Use the Present Perfect Tense

If you are not a native English speaker, it can be challenging to know when to use the present perfect tense. Here are the most common six situations that demand present perfect tense use.
An Ongoing Action That Started in the Past but Has Not yet Been Completed
People often use the present perfect tense to talk about uncompleted past actions. In this situation, the present perfect tense shows a past action with present effects.
For example:
- I have attended this school since I was seven years old.
In this situation, you could also use the present perfect continuous. So, how can you tell which of the two verb tenses is better suited?
- You use the present perfect continuous when the emphasis falls on the time length or the action itself.
- You use the present perfect when the emphasis falls on the consequences or effects of the action.
Suppose you’re having a conversation with someone and want to tell them where you’ve studied. You have two options:
“I’ve studied in London my entire life.”
In this situation, you’re telling them where you studied, using the normal present perfect.
If you want to emphasize how long you’ve studied in London, you use the present perfect continuous and say:
“I’ve been studying in London my entire life.”
A Series of the Same Action Completed Multiple Times in the Past, Likely to Happen Again in the Future
You can also use the present perfect tense when discussing an action that’s happened before and will likely happen in the future.
For example:
- She has listened to this song the entire week. (and she will likely listen to it again)
An Action That Was Completed Very Recently
You can use the present perfect tense to indicate something that has only been finished recently. Even if the event occurred in the past, it took place not long ago, meaning it directly affects the here and now.
In this scenario, people often use “now” or “just.” For example:
- I’ve just finished my dinner and want to go to bed.
- We have attended classes now and wanted to grab a bite to eat.
A Change Over Time
When you want to talk about something that has changed over a longer period, you use the present perfect tense.
For example:
- Your son has grown a lot since I last saw him.
An Uncompleted Action That Is Expected to Be Finished
The present perfect tense is also suitable for situations where action has started in the past but is not yet finished. You can also use this verb tense if the action is likely to be completed in the future.
To describe an uncompleted action waiting to be finished, you need to use the negative form of the verb.
For example:
- I haven’t read the book my teacher recommended.
To Add Significance to a Completed Action
The present perfect tense also works when you want to make past actions sound more significant. When talking about great accomplishments, rare or dramatic events, people also use the present perfect.
For example:
- Alexander Fleming has invented penicillin!
- I have been overwhelmed with fear!
The Present Perfect Tense for Statements
To make a statement using the present perfect tense, you must combine “have” or “has” with the past participle of the verb in question.
Example:
- I have become a good guitar player because I practiced a lot.
- We have had our difference before, but we’re good friends now.
The Present Perfect Tense for Negatives
The present perfect tense can be used for both positive and negative statements.
For example, “I have not finished my work” would also be written in the present perfect tense. In this sentence, “I” is the subject, “have not” is the negative form of the present tense of the verb “to have,” and “finished” is still the past participle of the verb “to finish.”
The formula for making a present perfect negative is “have/has” + negative + participle.
Here are some more examples:
- He has not seen his best friend in ages.
- You have not been sleeping properly, and it shows.
- They have not paid attention in class.
The Present Perfect Tense for Questions
When you want to form a question using the present perfect tense, you must place the auxiliary verb first. Continue with the subject and end with the past participle form of the main verb.
The formula is “have/has” + subject + past participle.
Here are some examples:
- Have you listened to the new Harry Styles album?
- Has Mary finished her shift yet?
When Not to Use the Present Perfect Tense
It’s quite common for people to confuse simple past and present perfect tenses because the main difference when using them is seeing whether the action is finished or not.
You should avoid using the present perfect tense with a specific time.
This means it’s incorrect to say, “You have studied last weekend.”
It’s correct to say, “You studied last weekend.”
If you want to correct the first sentence and still use a time frame, you could say something like “You have studied every weekend this month.”
Perfect Present Tense Examples in Sentences
Here are some more examples of how to properly use the present tense:
- We have played soccer professionally before.
- She has snuck some candy to class every day.
- I can’t stay any longer, my mom has cooked dinner.
- Have you eaten sushi before?
- I have never seen anything more beautiful in my entire life.
Final Thoughts
The present perfect tense is a verb form used to express an action or event that has occurred in the past and continues to affect the present. It can be used to talk about both completed and incomplete actions. I hope my guide helped you better understand the concept behind using present perfect tense!